9
ther adjustment is necessary. If not, then look through the
polar finder while rotating the mount about the R.A. axis.
You will notice that the object you have previously cen-
tered moves in a circular path. Use the three alignment
setscrews on the polar axis finder to redirect the
crosshairs of the polar finder to the apparent center of this
circular path. Repeat this procedure until the position that
the crosshairs point to does not rotate off-center when the
mount is rotated in R.A. Once this is accomplished,
retighten the thumbscrews.
The polar axis finder scope is now ready to be used. When
not in use, replace the plastic protective cover to prevent the
polar finder from getting bumped.
Using the Polar Axis Finder Scope
The reticle of the polar axis finder scope for the SkyView Pro
has a tiny star map printed on it that makes precise polar
alignment quick and easy. If you do not have a clear view of
Polaris from your observing site, you will not be able to use
the polar-axis finder to precisely polar align the telescope. To
align the mount using the polar axis finder scope, follow these
instructions:
1. Approximately polar-align the mount as outlined in the
procedure above.
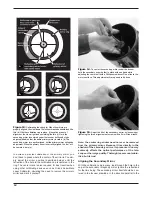
2. Loosen the Dec. lock lever and rotate the optical tube on
the declination axis so that the tube is at a 90° to the right
ascension axis (Figure 10). Tighten the Dec. lock lever.
3. Remove the cap on the front opening of the equatorial
mount (Figure 6). Focus the polar finder by rotating the
eyepiece. Now, sight Polaris in the polar axis finder scope.
If you have followed the approximate polar alignment pro-
cedure accurately, Polaris will probably be within the field
of view. If not, move the tripod left-to-right, and adjust the
latitude up-and down until Polaris is somewhere within the
field of view of the polar axis finder scope.
4. Shine a red flashlight down the front end of the polar find-
er to illuminate the reticle within the field of view. Make
sure the flashlight shines in at an angle, so as not to block
the polar finder’s field of view. It may be helpful to have a
friend hold the flashlight while you look through the polar
finder. Note the constellation Cassiopeia and the Big
Dipper in the reticle. They do not appear in scale, but they
indicate the general positions of Cassiopeia and the Big
Dipper relative to the north celestial pole (which is indicat-
ed by the cross at the center of the reticle). Rotate the ret-
icle so the constellations depicted match their current ori-
entation in they sky when viewed with the naked eye. To
do this, release the R.A. lock lever and rotate the main tel-
escope around the R.A. axis until the reticle is oriented
with sky. For larger optical tubes, you may need to remove
the tube from the mount to prevent it from bumping into
the mount. Once the reticle is correctly oriented, use the
right ascension lock lever to secure the mount’s position.
5. Now use the azimuth adjustment knobs (Figure 8) and the
latitude adjustment L-bolts (Figure 6) on the mount to
position the star Polaris inside the tiny circle marked
“Polaris” on the finder’s reticle. You must first loosen the
knob underneath the equatorial mount on the center sup-
port shaft to use the azimuth adjustment knobs. Once
Polaris is properly positioned within the reticle, you are
precisely polar aligned. Retighten the knob underneath
the equatorial mount.
Note: From this point on in your observing session, you
should not make any further adjustments in the azimuth
or the latitude of the mount, nor should you move the tri-
pod. Doing so will undo the polar alignment. The tele-
scope should be moved only about its right ascension
and declination axes.
Additional Note Regarding Focusing the Polar
Axis Finder Scope
The polar axis finder scope is normally focused by simply
rotating the eyepiece focus ring. However, if after adjusting
the focus ring you find that the image of the reticle is sharp,
but the stars are out of focus, then you must adjust the focus
of the polar axis finder’s objective lens. To do this, first remove
the polar axis finder from the mount. Look through the polar
axis finder at a star (at night) or distant object at least 1/4 mile
away (during daylight). Use the eyepiece focus ring to bring
the reticle into sharp focus. Now, loosen the focus lock ring
(Figure 9a) and thread the entire objective end of the finder
inwards or outwards until images appear sharp. Re-tighten
the focus lock ring. Once the polar axis finder’s objective lens
is focused, it should not need to be adjusted again.
Use of the Right Ascension and Declination
Slow-Motion Control Knobs
The right ascension (R.A.) and declination (Dec.) slow-motion
control knobs allow fine adjustment of the telescope’s position
to center objects within the field of view. Before you can use
the knobs, you must manually “slew” the mount to point the
telescope in the vicinity of the desired target. Do this by loos-
ening the R.A. and Dec. lock levers and moving the telescope
Figure 10.
The optical tube must be at a 90° angle to the right
ascension axis in order to view through the polar axis finder.
Содержание SKYVIEW PRO 6LT EQ 9872
Страница 19: ...19 ...