1. Loosen the Dec. lock lever and rotate the telescope until
the declination value from the star atlas matches the read-
ing on the Dec. setting circle. Remember that values of the
Dec. setting circle are positive when the telescope is point-
ing north of the celestial equator (Dec. = 0°), and negative
when the telescope is pointing south of the celestial equa-
tor. Retighten the lock lever.
2. Loosen the R.A. lock lever and rotate the telescope until
the right ascension value from the star atlas matches the
reading on the R.A. setting circle. Remember to use the
lower set of numbers on the R.A. setting circle. Retighten
the lock lever.
Most setting circles are not accurate enough to put an object
dead-center in the telescope’s eyepiece, but they should
place the object somewhere within the field of view of the find-
er scope, assuming the equatorial mount is accurately polar
aligned. Use the slow-motion controls to center the object in
the finder scope, and it should appear in the telescope’s field
of view.
The setting circles must be re-calibrated every time you wish
to locate a new object. Do so by calibrating the setting circles
for the centered object before moving on to the next one.
Confused About Pointing the Telescope?
Beginners occasionally experience some confusion about
how to point the telescope overhead or in other directions. In
Figure 1 the telescope is pointed north as it would be during
polar alignment. The counterweight shaft is oriented down-
ward. But it will not look like that when the telescope is point-
ed in other directions. Let’s say you want to view an object
that is directly overhead, at the zenith. How do you do it?
DO NOT make any adjustment to the latitude adjustment L-
bolts. That will spoil the mount’s polar alignment. Remember,
once the mount is polar aligned, the telescope should be
moved only on the R.A. and Dec. axes. To point the scope
overhead, first loosen the R.A. lock lever and rotate the tele-
scope on the right ascension axis until the counterweight
shaft is horizontal (parallel to the ground). Then loosen the
Dec. lock lever and rotate the telescope until it is pointing
straight overhead. The counterweight shaft is still horizontal.
Then retighten both lock levers.
What if you need to aim the telescope directly north, but at an
object that is nearer to the horizon than Polaris? You can’t do
it with the counterweights down as pictured in Figure 1. Again,
you have to rotate the scope in right ascension so that the
counterweight shaft is positioned horizontally. Then rotate the
scope in declination so it points to where you want it near the
horizon.
To point the telescope directly south, the counterweight shaft
should again be horizontal. Then you simply rotate the scope
on the declination axis until it points in the south direction.
To point the telescope to the east or west, or in other direc-
tions, you rotate the telescope on its right ascension and dec-
lination axes. Depending on the altitude of the object you want
to observe, the counterweight shaft will be oriented some-
where between vertical and horizontal.
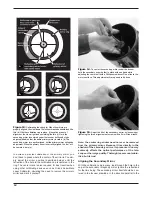
Figure 12 illustrates how the telescope will look when pointed
at the four cardinal directions: north, south, east and west.
7. Collimating
(Aligning The Mirrors)
Collimating is the process of adjusting the mirrors so they are
perfectly aligned with one another. Your telescope’s optics
were aligned at the factory, and should not need much adjust-
ment unless the telescope is handled roughly. Accurate mir-
ror alignment is important to ensure the peak performance of
your telescope, so it should be checked regularly. Collimating
is relatively easy to do and can be done in daylight.
To check collimation, remove the eyepiece and look down the
focuser drawtube. You should see the secondary mirror cen-
tered in the drawtube, as well as the reflection of the primary
mirror centered in the secondary mirror, and the reflection of
the secondary mirror (and your eye) centered in the reflection
of the primary mirror, as in Figure 13a. If anything is off-cen-
ter, as in Figure 13b, proceed with the following collimating
procedure.
The Collimation Cap and Mirror Center Mark
Your SkyView Pro 6LT EQ comes with a collimation cap. This
is a simple cap that fits on the focuser drawtube like a dust
cap, but has a hole in the center and a silver bottom. This
helps center your eye so that collimation is easy to perform.
Figures 13b through 13e assume you have the collimation
cap in place.
In addition to the collimation cap, the primary mirror is marked
with a circle at its exact center. This “center mark” allows you
11
Figure 12.
This illustration show the telescope pointed in the four cardinal directions (a) north, (b) south, (c) east, (d) west. Note that the
tripod and mount have been moved; only the telescope tube has been moved on the R.A. and Dec. axes.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Содержание SKYVIEW PRO 6LT EQ 9872
Страница 19: ...19 ...