13
length of the telescope. If it isn’t, as in Figure 13b, it must be
adjusted. This adjustment will rarely, if ever need to be done.
It helps to adjust the secondary mirror in a brightly lit room
with the telescope pointed towards a bright surface, such as
white paper or wall. Also placing a piece of white paper in the
telescope tube opposite the focuser (in other words, on the
other side of the secondary mirror) will also be helpful in colli-
mating the secondary mirror. Using a 2mm Allen wrench,
loosen the three small alignment set screws in the center hub
of the 4-vaned spider several turns. Now keep the mirror’s
holder stationary (be careful not to touch the surface of the
mirrors), while turning the center screw with a Phillips head
screwdriver (See Figure 14). Turning the screw clockwise will
move the secondary mirror toward the front opening of the
optical tube, while turning the screw counter-clockwise will
move the secondary mirror toward the primary mirror.
Note: When making these adjustments, be careful not to
stress the spider vanes or they may bend.
When the secondary mirror is centered in the focuser draw-
tube, rotate the secondary mirror holder until the reflection of
the primary mirror is as centered in the secondary mirror as
possible. It may not be perfectly centered, but that is OK. Now
tighten the three small alignment screws equally to secure the
secondary mirror in that position.
If the entire primary mirror reflection is not visible in the sec-
ondary mirror, as in Figure 13c; you will need to adjust the tilt
of the secondary mirror. This is done by alternately loosening
one of the three alignment set screws while tightening the
other two, as depicted in Figure 15. The goal is to center the
primary mirror reflection in the secondary mirror, as in Figure
13d. Don’t worry that the reflection of the secondary mirror
(the smallest circle, with the collimation cap “dot” in the cen-
ter) is off-center. You will fix that in the next step.
Adjusting the Primary Mirror
The final adjustment is made to the primary mirror. It will need
adjustment if, as in Figure 13d, the secondary mirror is cen-
tered under the focuser and the reflection of the primary mir-
ror is centered in the secondary mirror, but the small reflec-
tion of the secondary mirror (with the “dot” of the collimation
cap) is off-center.
The tilt of the primary mirror is adjusted with three spring-
loaded collimation thumbscrews on the back end of the opti-
cal tube (bottom of the primary mirror cell); these are the larg-
er thumbscrews. The other three smaller thumbscrews lock
the mirror’s position in place; these thumbscrews must be
loosened before any collimation adjustments can be made to
the primary mirror.
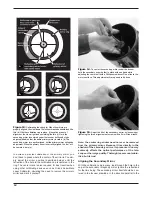
To start, turn the smaller thumbscrews that lock the primary
mirror in place a few turns each (Figure 16). Use a screwdriv-
er in the slots, if necessary.
Now, try tightening or loosening one of the larger collimation
thumbscrews with your fingers (Figure 17). Look into the
focuser and see if the secondary mirror reflection has moved
closer to the center of the primary. You can tell this easily with
the collimation cap and mirror center mark by simply watch-
ing to see if the “dot” of the collimation cap is moving closer or
further away from the “ring” on the center of the primary mir-
ror mark. When you have the dot centered as much as is pos-
sible in the ring, your primary mirror is collimated. The view
through the collimation cap should resemble Figure 14e. Re-
tighten the locking thumbscrews.
A simple star test will tell you whether the optics are accurate-
ly collimated.
Star-Testing the Telescope
When it is dark, point the telescope at a bright star and accu-
rately center it in the eyepiece’s field-of-view. Slowly defocus
Figure 16.
The three small thumbscrews that lock the primary
mirror in place must first be loosened before any adjustments can be
made. A flat head screwdriver may be used to loosen these screws.
Figure 17.
The tilt of the primary mirror is adjusted by turning
one or more of the three larger thumbscrews.
Содержание SKYVIEW PRO 6LT EQ 9872
Страница 19: ...19 ...