IPF
Page 8
4. Repeat steps 1 through 3 until IPF outputs 0% of
rated pressure range at 0% current input, and
100% of output pressure range at 100% current
input.
5. Verify the accuracy of your adjustments by
inputting the appropriate percent of span levels
listed in table 3.
Installation
The installation of the IPF is carried out in three
phases. The first phase is the physical mounting of
the unit. Next is the electrical connections phase,
and finally, pneumatic connections can be made. It
is strongly recommended that IPF’s be installed in
this order.
It is also strongly suggested that each unit be
calibrated according to the instructions in this manual
before being placed into service.
The IPF may be installed at any angle; either sur-
face-mounted, or attached to pipe or round conduit.
Consideration should always be given to any require-
ment that may arise for front panel access, checking
the fittings, or reading the FR1 Option gauge and
draining its filter.
Closed Loop/Open Loop.
The IPF should be
installed in a closed loop. A closed loop is the best
way to measure a control variable, to determine if a
deviation from a desired value exists, or to automati-
cally provide feedback for actuator loading pressure.
An open loop has inherent limitiations that are not
consistent with precise control. Long term drift of the
loop dynamics, load fluctuations that require constant
adjustments of the actuator loading pressure, and
performance quality variations due to inconsistencies
between operating personnel are all problems
commonly associated with open loops. A controlled
variable cannot be directly measured in an open
loop; this prevents compensating adjustments to the
system input.
Mounting
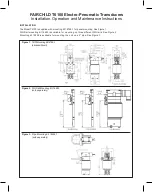
Figure 3 gives the IPF’s outline dimensions. The
illustration also gives the dimensions of the available
FR1 Option hardware, recommended for most
installations, and the external sub-housing used for
the terminal block with NE-type IPF’s.
After placing the IPF in the desired location and
orientation, secure the housing with the optional pipe
mounting hardware, or other appropriate fasteners.
Figure 4 illustrates IPF mounting using optional pipe
mounting hardware. Note that the holes in the
mounting plate that comprises the base of the IPF
are symmetrical. This allows the unit to be installed
on either horizontal or vertical pipes.
The thermoplastic polyetherimide compound used in
the housing provides excellent protection from
chemical exposure. The housing is also unaffected
by electrolytic corrosion, as may be found in and
around salt water and many other industrial environ-
ments. Note, however, that this type of IPF is
designed, tested, and built for installation outdoors or
in well ventilated areas.
Refer to the WP/WPM housing data sheet in the
Moore Industries Product Catalog for more informa-
tion regarding chemical environments compatibility,
or contact your Moore Industries Sales Representa-
tive for assistance.
Electrical Connections
Refer to figure 1 in the Calibration Setup Section of
this manual for instruction on the level of disassem-
bly required to make the electrical connections to the
IPF.
Figure 5 is a generic diagram showing the unit’s
installation hookup.
To complete connections, route wiring through
conduit port, or through port in sub-housing for NE-
type units, to terminal block, and use a slotted-tip
screwdriver with a maximum head width of 3 mm
(0.125 inch) to loosen the terminal screws.