MC2-30M
Doc. N°
MO-0495-ING
Copyright 2018
Date
17.03.2022
Rev.
2
Pag. 34
of
64
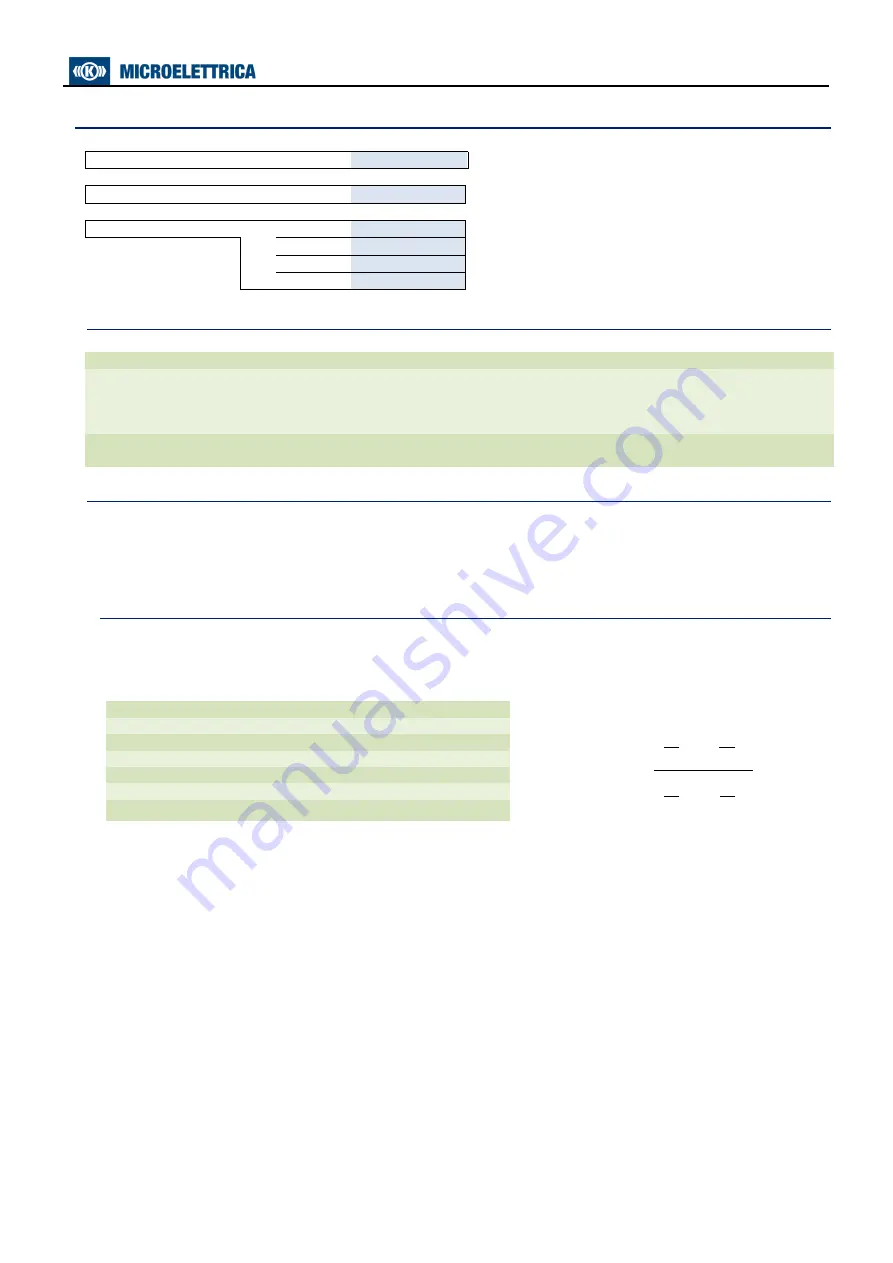
17.6 - Function:
T>
(Thermal Image F49)
Status
→
Enab.
No
[No / Yes]
Options
→
OPMOD
I1.I2
[I1.I2 / I.Max]
Livelli
→
Tal
50
%Tb
[10
÷
100]
step 1
%Tb
→
Is
1
In
[0.5
÷
1.5]
step 0.01 In
→
Tres
50
%Tb
[10
÷
100]
step 1
%Tb
→
To
1
nkt
[1
÷
10]
step
1
nkt
17.6.1 - Description of variables
Abil.
: Function enabling (No = Disable / Yes = Enable)
OPMOD
:
I1.I2
= Direct/Inverse current
I.Max
= Phase current
Tal
: Temperature pre-alarm level
Is
: Continuous admissible current
Tres
: Temperature reset
To
: Warming-up Time Constant of the load
17.6.2 - Trip and Alarm
The algorithm compares the amount of heat accumulated “T” (
≡
i
2
•
t) to the steady state amount of heat “Ts”
corresponding to continuous operation at the continuously admissible current “Is”.
When the ratio “T/Ts” reaches the level set for Thermal Alarm “Tal” of the max allowed heating, the relay
trips accordingly
17.6.2.1 – Trip time of the Thermal Image Element
The trip time of the Thermal Image Element is a function of the current “I” flowing into the load and
depends on its warming-up Time Constant “Kt”, on the previous thermal status “Ip” and on the maximum
admissible continuous current “Is” according to the equation:
t
= Time to relay tripping
Kt
= Load thermal time constant
I
= Actual load current
In
= Load rated current
Is
= Continuous admissible current
Ip
= Steady state current before the overload
n
= Natural Logarithm
When the heating exceeds the set alarm level “Tal” or the max. allowed level (“I” > “Is” for the time “t”)
the output relays programmed for these function will be operated. Reset will take place when the thermal
status will drop below 95% of the trip level.
2
2
2
2
n
In
Is
In
I
In
Ip
In
I
K
t
−
−
⋅
=
t
















































