32
SySTEM
3.3 THEORy
Water is a major component of foods, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics and influences the
product texture, appearance, flavor, and shelf life. Quantifying these attributes require two
basic types of water analysis: moisture content and water activity (
a
w
).
3.3.1 WATER ACTIVITy
Water activity (
a
w
) is a measurement of the energy status of the water in a system. The
value indicates how tightly water is bound, structurally or chemically, within a substance.
The concept of water activity is of particular importance in determining product quality
and safety. It predicts safety and stability with respect to microbial growth, chemical and
biochemical reaction rates, and physical properties.
Water activity is a measure of the energy status of the water in a system and is a far better
indicator of perishability than moisture content.
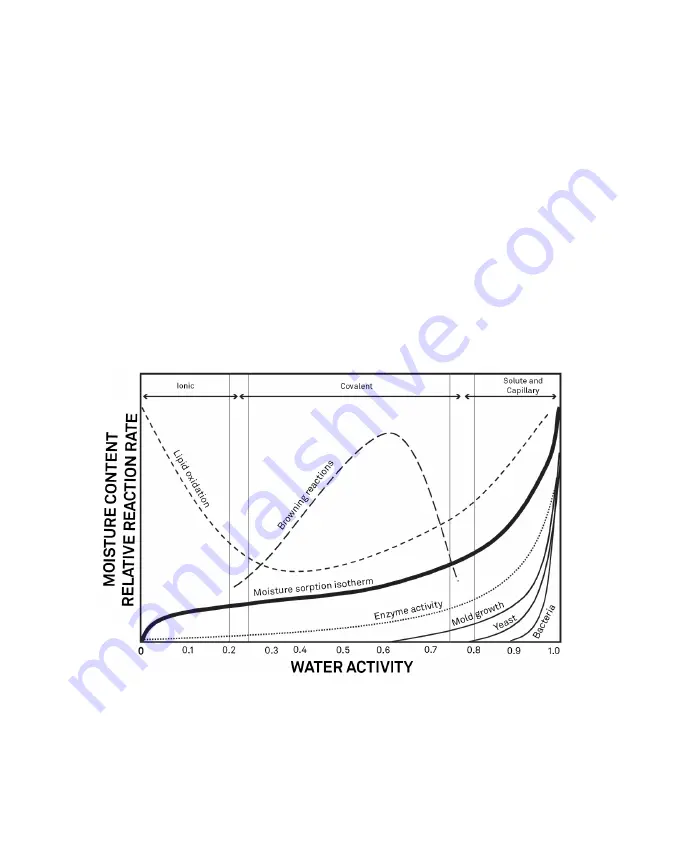
shows how the relative activity
of microorganisms, lipids, and enzymes relate to water activity. While other factors, such as
nutrient availability, temperature, and pH, can affect the relationships, water activity is the
best single measure of how water affects these processes.
Figure 46 Water activity diagram adapted from Labuza
Researchers measure the water activity of a system by equilibrating the liquid phase water
in the sample with the vapor phase water in the headspace and measuring the relative
humidity of the headspace. In the AQUALAB TDL, a sample in a sample cup is sealed inside
the sample chamber, which contains a tunable diode laser and an infrared thermometer.
The AQUALAB TDL determines the vapor pressure in the headspace and the infrared
thermometer measures the sample temperature. From these measurements, the relative
















































