The repair methods given by the manufacturer in this document are based on the technical specifications, current at the time of release. The methods may be modified as a result of changes introduced by the manufacturer in the production of the various component
units and accessories from which the vehicles are manufactured. The reproduction, translation, transmission, in part of or whole of the present document,are prohibited without the prior written consent of Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd. The use of this document by any
person other than the trained personnel, at the Authorized Service Centre of Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd.,will amount to unauthorized use and shall be liable for penalty/prosecution
© 2013 Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd.
MAN-00233
MAY 2013/Rev 1
WIRING MANUAL
25042013
Voltage:
Voltage is the potential difference (electromotive force) between two points in a circuit.
Overview
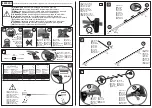
This meter is connected to measure battery voltage.
Example:
you place the probes of a DMM on the
terminals of a battery, you are measuring
the Potential difference, or electromotive
force, or voltage, between the positive and
negative terminals
Applications of voltage
−
Technicians are concerned with voltage in different applications:
•
Source voltage
•
Available voltage
•
Voltage drop
Source voltage
−
the battery supplies source voltage in most automotive electrical systems.
Measuring voltage
−
use the DMM to measure voltage. Note that voltage measurements
are made by placing the voltage leads in a parallel circuit to the circuit you are testing.
Available voltage
−
is the voltage in a circuit available to operate the load.
Voltage drop
−
most parts of an electrical circuit offers some resistance to current. Every
element that has resistance causes a voltage drop. Voltage drop increases as resistance
increases.
ESSENTIAL ELECTRICAL CONCEPTS
191