Lantronix
SM12XPA Web User Guide
33848 Rev. A
Page
94
of
473
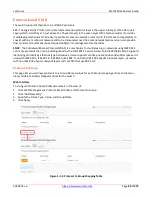
Stream
This page lets you configure 1-10 Stream instances. A Stream is described as the path through the network from
“Talker” to “Listener.”
Navigate to the VLAN Management > Stream > Stream menu path. Click the Add New Stream (
) button and
enter the desired parameters. Click Apply when done.
Stream Reservation Protocol (SRP) is an enhancement to Ethernet that implements admission control.
In September 2010 SRP was standardized as IEEE 802.1Qat which has subsequently been incorporated into IEEE
802.1Q-2011. SRP defines the concept of streams at layer 2 of the OSI model. Also provided is a mechanism for
end-to-end management of the streams' resources, to guarantee quality of service (QoS). SRP is part of the IEEE
Audio Video Bridging (AVB) and Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) standards.
SRP registers a stream and reserves the resources required through the entire path taken by the stream, based
on the bandwidth requirement and the latency which are defined by a stream reservation traffic class.
Listener (stream destination) and Talker (stream source) primitives are utilized. Listeners indicate what streams
are to be received; Talkers announce the streams that can be supplied by a bridged entity. Network resources
are allocated and configured in both end nodes of the data stream and the transit nodes along the data streams'
path. An end-to-end signaling mechanism to detect the success/failure of the effort is also provided.
An SRP "talker advertise" message includes QoS requirements (e.g., VLAN ID and Priority Code Point (PCP)) to
define traffic class, rank (emergency or nonemergency), traffic specification (maximum frame size and maximum
number of frames in a traffic class), measurement interval, and accumulated worst case latency).
Talker advertise and listener ready messages can be de-registered, which terminates the stream. Periodic polling
of advertise and ready messages is used to detect unresponsive devices.
SRP works using the Multiple MAC Registration Protocol (MMRP), the Multiple VLAN Registration Protocol
(MVRP), and the Multiple Stream Registration Protocol (MSRP). MMRP controls propagation of group
registration, and MVRP controls VLAN membership (MAC address information). MSRP works in a distributed
network of bridges and end stations; it registers and advertises data streams and reserves bridge resources to
provide the QoS guarantees.
A station (talker) sends a reservation request with the general MRP application. All participants in the stream
have an MSRP application and the MRP Attribute Declaration (MAD) specification for describing the stream
characteristics. Then each bridge within the same SRP domain can map, allocate, and forward the stream with
the necessary resources by using the MRP attribute propagation.
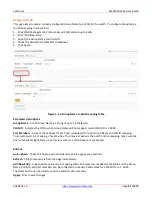
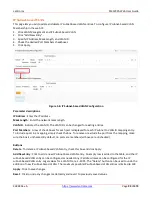
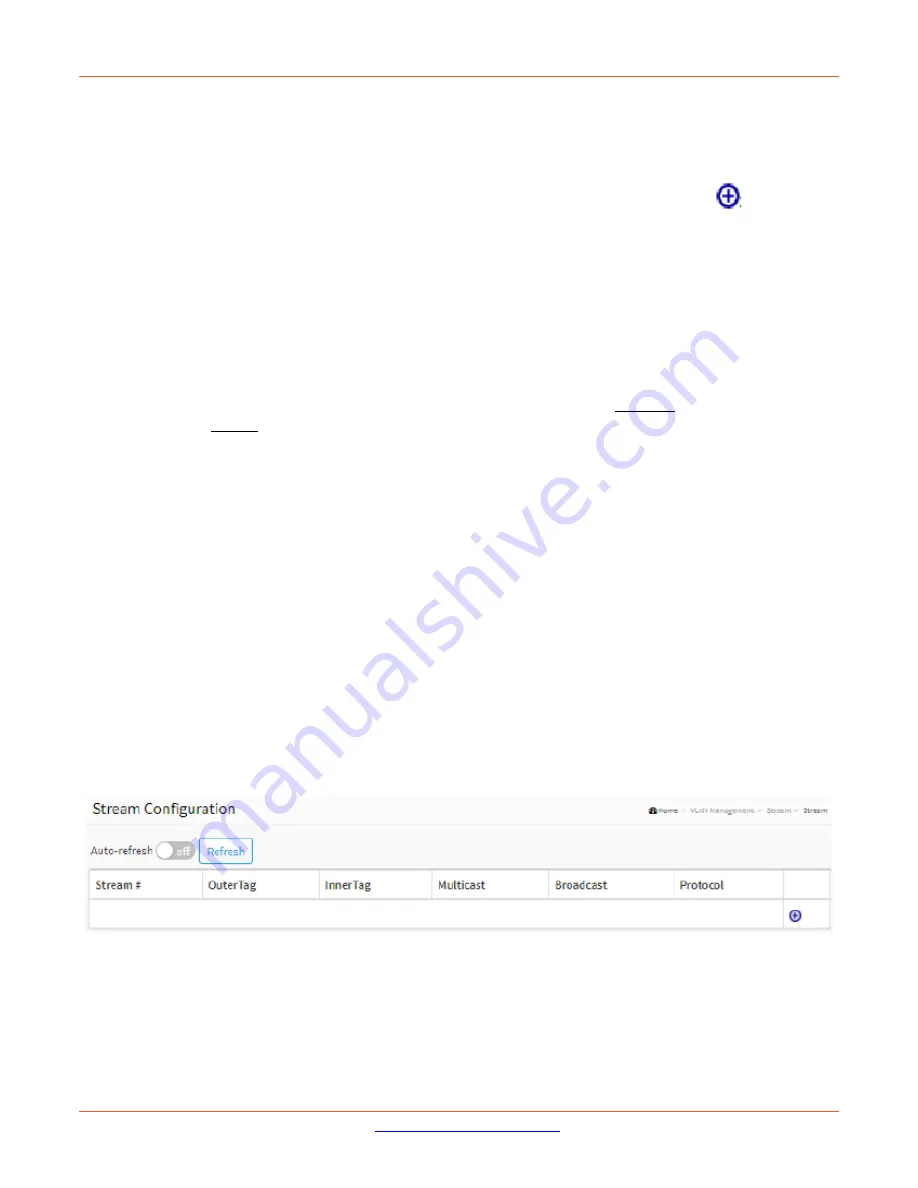
Figure 4-7.1: Stream Configuration
Parameter descriptions
:
Stream #
: The ID of the Stream. Valid values are 1 - 10.
OuterTag
: The outer tag in the SRP streaming data frames to be propagated from Talker to Listener.
InnerTag
: The Inner tag in the SRP streaming data frames to be propagated from Talker to Listener.