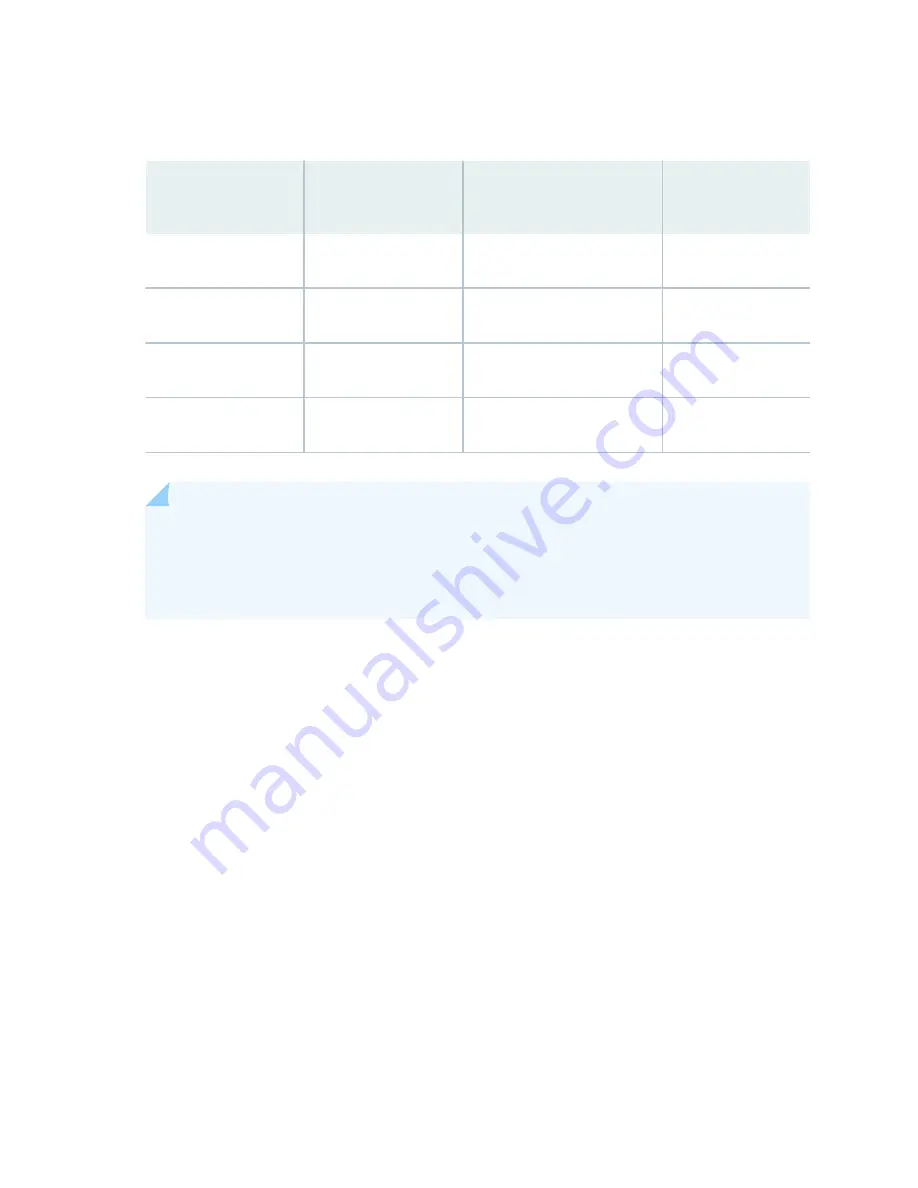
Table 36: Power Voltage Settings for JNP10K-PWR-AC2 and JNP10K-PWR-DC2 Power Supplies
(Continued)
INP0 (Switch 1)
INP1 (Switch 2)
H/L (High-Input/
Low-Input Switch 3)
Output Power
On
Off
On (High 80 A)
2750 W
Off
On
On (High 80 A)
2750 W
On
Off
Off (Low 60 A)
2200 W
Off
On
Off (Low 60 A)
2200 W
NOTE: If any JNP10K-PWR-AC2 power supply is set to 20 A, then the power budget for all
power supplies installed in the system becomes 20 A, regardless of whether other power
supplies are set at 30 A. This design is to prevent overloading of the power supply that is set
to 20 A. See
for details on setting the DIP switches.
2. Determine the total power required for your configuration with line cards installed. The total power
available to the chassis is calculated by dividing the wattage needed by the power rating, and then
rounding up.
In the previous examples, we calculated that an MX10004-PREMIUM system requires 10082 W with
four MX10K-LC9600 line cards. In this example, we calculate the total power available for two
JNP10K-PWR-AC2 power supplies set for dual feed and low power in an MX10004-PREMIUM
configuration:
10082 W (premium system) / 3000 W (6000 W total, 3000 per device) = 3.36
Round up the result to three JNP10K-PWR-AC power supplies. An MX10004-PREMIUM redundant
AC system then has a sufficient number of power supplies.
3. Calculate how much power the power supplies need. To determine the power required, multiply the
number of power supplies by the power supply wattage that each supply requires. Then, divide by
the efficiency of the power supply. The efficiency rate accounts for the loss of energy within the
power supply and is 89 percent for power supplies running in MX10004 routers.
94
















































