33
in the processor cache, accesses with the aperture range are forwarded to the main memory,
then PAC will translate the original issued address via a translation table that is maintained
on the main memory. The option allows the selection of an aperture size of 32MB, 64MB.
3-6-1 SDRAM Timing Setting
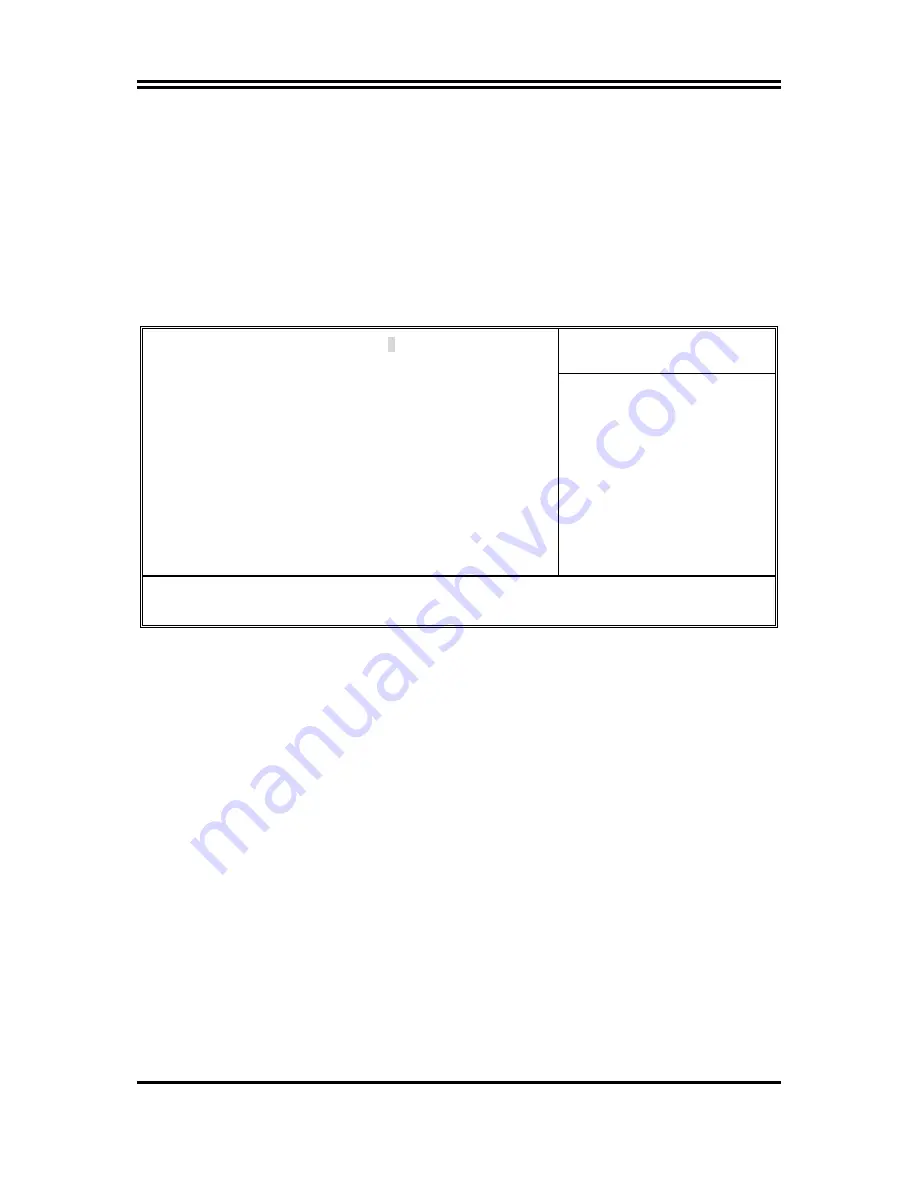
CMOS Setup Utility – Copyright(C) 1984-2000 Award Software
SDRAM Timing Setting
Item Help
SDRAM CAS Latency Time 3
SDRAM Cycle Time Tras/Trc 6/8
SDRAM RAS-to-CAS Delay 3
SDRAM RAS Precharge Time 3
DRAM CTL Buffer strengths Normal
DRAM MD Buffer strengths Normal
Menu Level >>
When set to “Auto”,
BIOS will program this
Timing mainly by the
SPD method. SPD means
“Serial Presence
Detect”, which enables
the BIOS to access
the manufacturer
settings stored in
DRAM module.
↑↓→←
Move Enter:Select Item +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Optimized Defaults F7:Standard Defaults
SDRAM CAS Latency Time
When synchronous DRAM is installed, the number of clock cycles of CAS latency depends
on the DRAM timing. The settings are: 2 and 3.
SDRAM Cycle Time Tras/Trc
Select the number of SCLKs for an access cycle. The settings are: 5/7 and 6/8.
SDRAM RAS-to-CAS Delay
This field let’s you insert a timing delay between the CAS and RAS strobe signals, used
when DRAM is written to, read from, or refreshed. Fast gives faster performance; and
Slow gives more stable performance. This field applies only when synchronous DRAM is
installed in the system. The settings are: 2 and 3.
SDRAM RAS Precharge Time
If an insufficient number of cycles is allowed for the RAS to accumulate its charge before
DRAM refresh, the refresh may be incomplete and the DRAM may fail to retain date. Fast
gives faster performance; and Slow gives more stable performance. This field applies only
when synchronous DRAM is installed in the system. The settings are: 2 and 3.
















































