5
Chargemaster Pinner
5200710 Rev. H
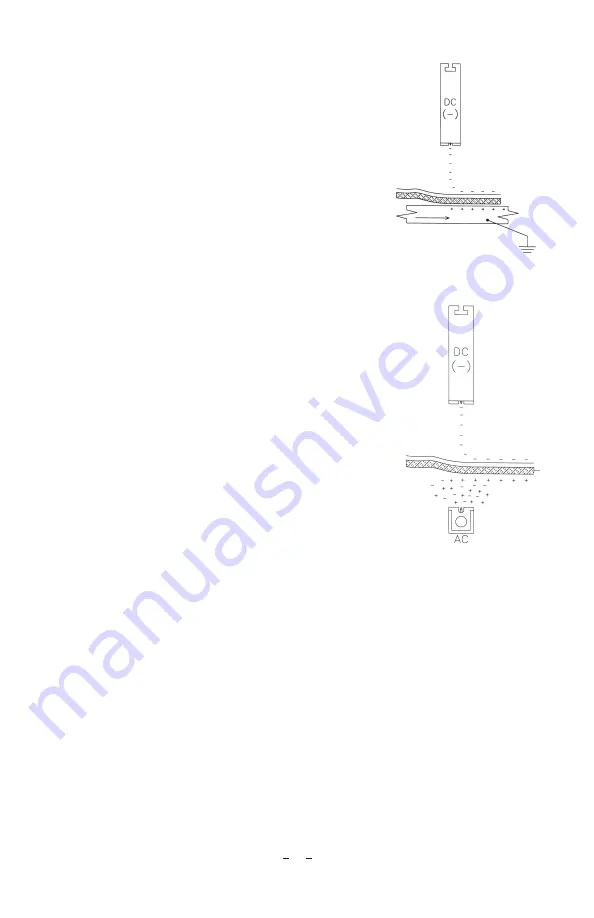
In
Figure 2
, the charging bar faces a production
fixture that moves beneath the charging bar
(alternatively the bar could move over the fixture)
in an interleaving application where paper or film
is pinned to metal prior to cutting and stacking.
After the materials to be pinned together are
positioned on the fixture, it moves beneath the
charging bar. The negative ions created by the
bar are driven toward the grounded metal fixture
by an electric field formed between them. The
top material blocks ion travel through the field
and becomes electrostatically charged, resulting
in adhesion between the two materials and the
fixture.
Option 2: Charging Bar with Static
Neutralizing Bar
In
Figure 3
, the charging bar faces an insulative
film while a static neutralizing bar faces an
insulative sheet of material on the opposite side
(glass, plastic, light particle-board, etc.). As the
two materials to be pinned together pass between
the bars, the negative ions created by the charging
bar charge the film, while the static neutralizing
bar attempts to eliminate the apparent charge on
the sheet. This deposits a positive charge on the
lower sheet. The use of the static neutralizing bar
dramatically improves the electrostatic pinning
adhesion between the two materials.
Figure 2
Figure 3
















