3.3. General Operations
3.3.1. Specifying Operational Mode
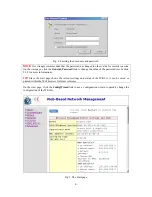
Fig. 22. Operational modes.
On this page, you can specify the operational mode for the WIASA. Currently, 5 modes are available:
Simple Access Point.
In this mode, the Ethernet WAN interface is disabled. The WIASA
acts as a bridge between the Ethernet LAN interface and the IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN inter-
face.
Router with a PPPoE-based DSL/Cable Connection.
In this mode, the WIASA assumes
that a DSL or cable modem is connected to its Ethernet WAN interface. The client computers
can therefore share this DSL/cable-based Internet connection by the NAT server functionality.
The IP address of the Ethernet WAN interface is obtained automatically by PPPoE from the ISP.
Router with a DHCP-based DSL/Cable Connection.
In this mode, the WIASA assumes
that a DSL or cable modem is connected to its Ethernet WAN interface. The client computers
can therefore share this DSL/cable-based Internet connection by the NAT server functionality.
The IP address of the Ethernet WAN interface is obtained automatically by DHCP from the ISP.
Router with a Static-IP DSL/Cable Connection.
In this mode, the WIASA assumes that a
DSL or cable modem is connected to its Ethernet WAN interface. The client computers can
therefore share this DSL/cable-based Internet connection by the NAT server functionality. The
IP address of the Ethernet WAN interface must be manually set.
Router with a Dial-up Connection.
In this mode, the WIASA assumes that a V.90 modem
or ISDN TA is connected to its RS232 (COM) port. The client computers can therefore share
this V.90/ISDN-based Internet connection by the NAT server functionality.
TIP:
When you have selected the operational mode of the WIASA, go to the
TCP/IP, Addressing
section of the management UI (see Section 3.4.1) to configure the addressing settings of the WAN
and LAN interfaces.
23