7
1. Determine the specifications of each cable
based on the
Schematic Diagram
delivered
with the product and Appendix A.
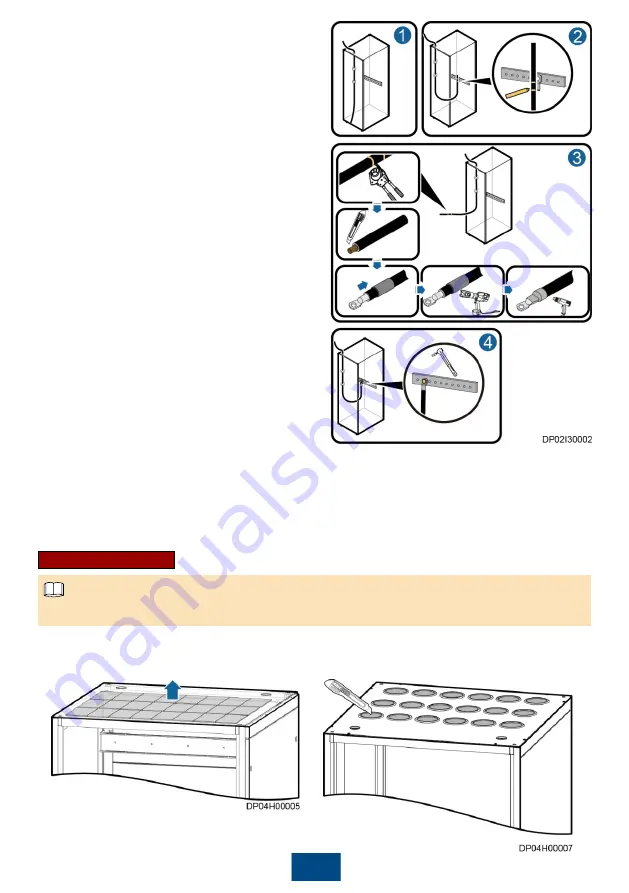
2. Route a cable into the cabinet and bind it to a
nearby beam, as shown by (1) in the figure.
3. Pull the cable to the copper bar to which the
cable will be connected, determine the cable
length, and label the cable, as shown by (2) in
the figure.
a. Mark a line where the cable is to be cut.
b. Mark a line where the cable is to be
stripped.
4. Pull the labeled cable outside of the cabinet,
and cut off the extra part at the marked line, as
shown by (3) in the figure.
5. Strip the cable at the marked line, and prepare
terminals.
6. Connect the input cables based on the
Schematic Diagram
delivered with the product,
as shown by (4) in the figure.
a. Route the input phase cables, N cable, and
PE cable into the PDC.
b. Connect the input N cable and PE cable to
the corresponding N bar and PE bar.
c. Connect the phase cables to the
corresponding input terminals of phases L1, L2,
and L3.
7. Connect the output cables based on the
Schematic Diagram
delivered with the product,
as shown by (4) in the figure.
a. Connect one PE cable and one N cable from the PE bar and N bar inside the PDC to each
load.
b. Connect the output power cable from the wiring terminal of the PDC output terminal block to
the corresponding load.
8. Connect the signal cables based on the
Schematic Diagram
delivered with the product.
9. Clear foreign matter inside the cabinet.
1. (Optional) Remove the rodent-proof meshes or cut crosses in wire bushings in the top cabling
scenario.
Removing a rodent-proof mesh
Cutting a cross in a wire bushing
Routing Cables
The figures are for reference only. The onsite objects prevail.
NOTE
2. (Optional) Remove the rodent-proof meshes or cut crosses in wire bushings
in the bottom cabling scenario.




































