Installer’s Information Manual
Page 9
DIRECT-VENT TERMINATION
You may terminate vent and combustion air pipes either
vertically (through the roof) or horizontally (through a side
wall). Vertical (through the roof) venting is preferred
because it offers protection from pipe damage and
condensate damage. You may use concentric vent
termination except on 126,000 BTU input furnaces. Follow
the instructions supplied with the concentric-vent kit.
For vertical direct venting, combustion air inlet pipe must
terminate next to vent pipe and 12 inches above roof (18” in
Canada) or highest expected snow accumulation. Extend
vent pipe at least 6 inches above combustion air inlet. See
Figure 4a for vertical direct vent termination.
Figure 4a. Vertical Termination for Direct Venting.
Combus tion-air-inlet termination must always be pointed
downward to keep out rain and snow. Fu rnace will not
operate properly with water in combustion compartment.
Note: When properly installed, vent pipe is designed to
drain condensate and will not be affecte d by rainwater.
For horizontal direct venting, combustion air inlet must
terminate next to vent pipe and at least 12 inches above
grade or highest expected snow accumulation. Extend vent
pipe at least 12 inches above combustion air inlet. See
Figure 4b.
Figure 4b. Horizontal Termination for Direct Venting.
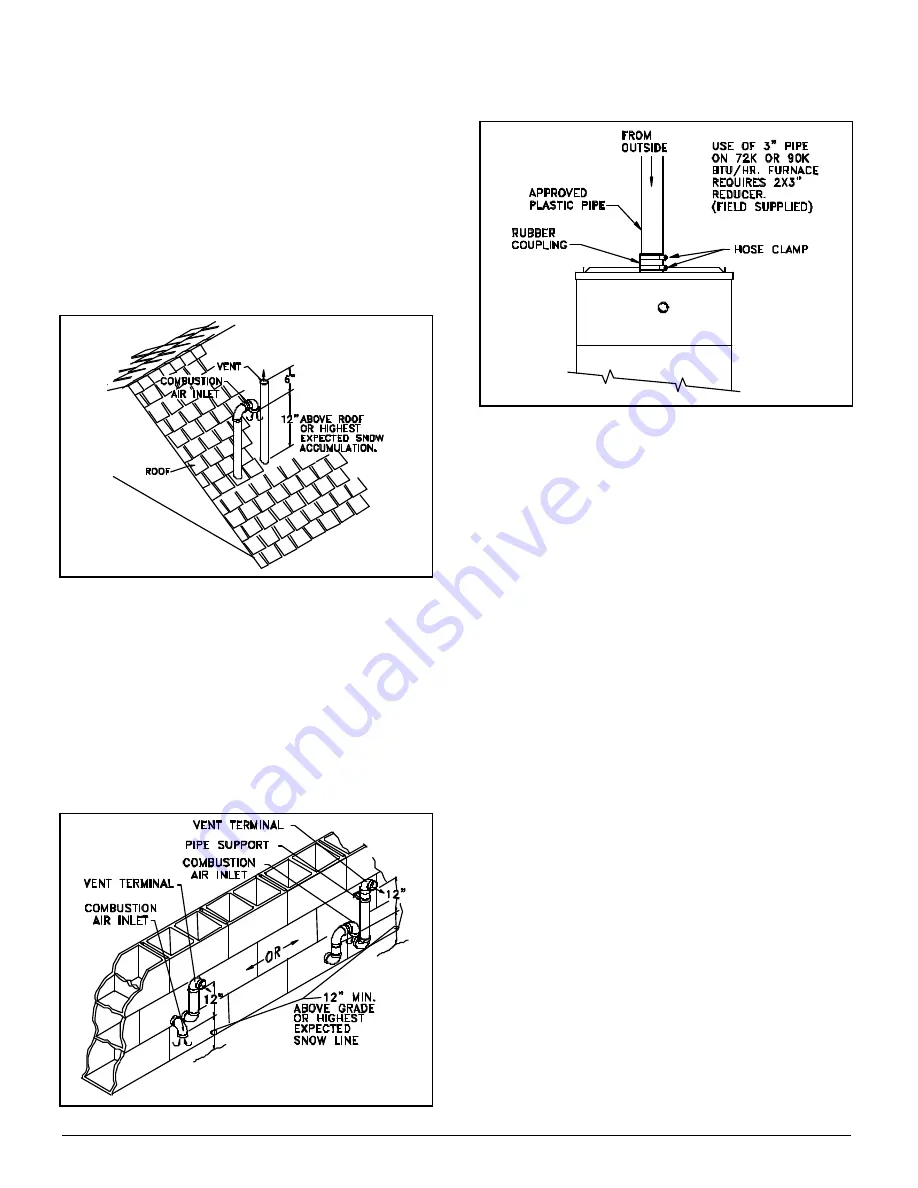
Attach a combustion air pipe to combustion-air-inlet collar
on top of furnace. Use rubber coupling and hose clamps
supplied with fu rnace. See Figure 5.
Figure 5. Combustion Air Pipe Connection to Fu rnace for
Direct Vent.
NON-DIRECT VENTING INSTRUCTIONS
(one pipe system)
DETERMINING VENT LENGTH
See Table 2 for maximum vent pipe length. Include any
termination elbows when determining maxim um allowable
vent length. Minimum pipe length is five feet with 0 elbows.
Table 2 shows the maximum allowable pipe length for non-
direct vent systems depending on:
??
altitude (elevation) of the installation
??
gas input rating of furnace
??
diameter of the vent pipe
??
number of elbows
Note that some of the larger furnace models may require a
high altitude pressure switch at elevations between 3000
and 6000 feet. For example, the chart shows that the
126,000 Btu/hr model may need a high altitude pressure
switch when installed at elevations between 3000 and 4000
feet. Above 4000 feet, this model requires a high altitude
switch for all installations.
All furnace models require the high altitude pressure switch
when installed at elevations above 6000 feet.
The high-altitude pressure switch is supplied with the LP
Conversion Kit #4226000 and the Natural Gas Conversion
Kit #4225600. These kits also contain the other
components required for furnace installation at high
elevations.
NOTE: Table 2 assumes Sweep 90
?
elbows like that in
Figure 3a. If using Hard 90
?
elbows similar to the one in
Figure 3b, decrease the vent length by 3 feet for every
elbow used.

































