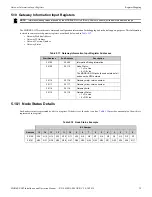
MODBUS-GW Installation and Operation Manual —
P/N LS10015-000NF-E:C2 4/30/2019
29
Section 4 Operation
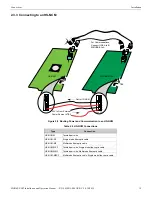
4.1 Panel and Gateway Synchronization
When making programming changes to a panel, it is important to verify that the MODBUS-GW has synchronized with these changes.
This assures reliable data from the gateway. There are several ways in which a MODBUS-GW synchronizes with a panel:
• The gateway attempts to compare its database with the panel database every 24 hours. If there is a difference, the gateway
synchronizes with the panel.
• If the gateway receives a message from the panel that it has been reprogrammed through a programming tool or from the front
panel, the gateway will attempt to resynchronize.
• If the gateway is reset, the power is cycled or the panel connectivity is lost and reapplied.
Resynchronization includes the following processes:
• The gateway updates all of its device type registers to match the panels.
• The gateway updates the device status registers to ensure the gateway provides accurate state data.
If the panel and panel network are not completely stable while the gateway is resynchronizing, the gateway aborts resynchronization.
4.2 Modbus Command Support
4.2.1 Modbus Commands
The MODBUS-GW supports the following Modbus commands:
• Read Input Registers (0x04)
• Read Holding Registers (0x03)
• Write Single register (0x06)
• Read Device Identification supported 43 / 14 (0x2B / 0x0E)
4.2.2 Exception Responses
The MODBUS-GW sends exception responses to its Modbus clients as appropriate (e.g., invalid command, invalid data, etc.). For more
information, refer to
Appendix B, “Exception Responses”
.
4.3 Modbus Addressing
The MODBUS-GW uses Modbus addressing within the following guidelines:
• The MODBUS-GW operates similarly to a Modbus bridge. Each MODBUS-GW can support up to four panels on an NFN network.
Each fire panel being addressed by the Modbus master on the NFN network is identified by the Unit ID.
• The Unit ID used in the MODBUS-GW must be in the range 1 through 247. This is a Modbus range limitation. The Unit ID should
match the node number of the NFN node that is being addressed. For example, a Unit ID of 127 addresses NFN node 127.
• The MODBUS-GW communicates on standard Modbus IP port 502.
• Standard register types and reference ranges are:
– 0x Coil 00001–09999
– 1x Discrete Input 10001–19999
– 3x Input Register 30001–39999
– 4x Holding Register 40001–49999
For more information on Modbus addressing, refer to
NOTE:
Communication on Modbus IP port 502 is not configurable and is a Modbus norm.