2-12
GB
In parallel with the CTL head is the RC cell comprising capacitor
[2479] and resistor [3471]. The capacitor [2479], together with the
CTL head inductivity, causes a resonance step-up at around 10
kHz and the resistor [3471] suppresses this step-up. This creates
an aperiodic transient response in the resonance. Beyond the
resonance frequency, there is an adjustment in terms of a steep fall
in the frequency transmission characteristic. This effectively
suppresses high-frequency pick-ups. The CTL head signal
amplitude in standard play is around 1mVp (typ.) which means that
the amplification for the playback amplifier must be
correspondingly high. To avoid offset problems, a 100 µF
electrolytic capacitor [2490] is fitted in the negative feedback
branch for DC decoupling.
The polarity of the playback amplifier can be changed using the
Video Index Search System (VISS) voltage. This is the only way in
which the µP can write a VISS mark on the tape without spikes. The
Write/Read (W/R) signal is used to switch over between record and
playback:
W = “H“, R = “L“.
4.2 Power on reset (POR) generator
The POR generator contained in the M63100FP [7463] requires
only one external capacitor [2477], which specifies the length of the
POR pulse. For 33 nF, t
POR
is approx. 30ms.
The response threshold of the reset circuit is between 4.5 and 4.8
V. Supply fluctuations which are shorter than tPOR/100 area and
which do not fall below 4.0 V, do not trigger the POR. The µP is
reset using the inverted POR.
4.3 The sensor interface :
The four comparators in the M63100FP [7463] are used to convert
sensor signals to the logic level. The outputs are overload
protected by a current limiter and thermal overload protection. Only
the non-inverting input on each comparator is accessible from the
outside. The other inputs are connected to an internal reference of
2.5V. The fixed hysteresis of the comparators of approx. 18 mV is
also located internally.
The comparators are connected as follows:
Comparator 1: In = FTA, pin 39; Out = FTAD, pin 34:
FTA = threading tachometer. This signal comes from a forked light
barrier in the deck. An infra-red light beam is interrupted by a 4-
blade impeller (butterfly). The output amplitude for the light barriers
should be less than 2V for the low level and greater than 3V in the
high level to ensure a correct evaluation process. An additional
hysteresis is created with a resistor [3476]. For unit versions <1W
and FOME the external operation amplifier [7530B] is used to
reduce the power consumption in <1W mode.
Comparator 2: In = WTR, pin 38; Out = WTRD, pin 33:
WTR = Winding tachometer right, from a reflection photoelectric
barrier. The level is the same as for the FTA.
Comparator 3: In = WTL, pin 37; Out = WTLD, pin 31 :
WTL = Winding tachometer left, from a reflection photoelectric
barrier. The level is the same as for the FTA.
Comparator 4: In = FG, pin 35; Out = FGD, pin 30:
FG = capstan tachometer. This signal stems from an amplifier for
the tachometer hall sensor on the motor unit [1946 pin 4]. The
output impedance is 10 kOhm. The amplitude of the virtually
sinusoidal signal is normally 1 Vp. It should not fall below 300
mVpp. It is AC-coupled via a capacitor [2485]. In order for a bias
current to flow, the input pin 31 must be passed via a resistor [3474]
to the reference voltage on pin 4. A capacitor [2480] for filtering out
high-frequency interference is arranged in parallel to the bias
resistor.
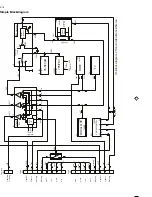
4.4 Interface to the head drum motor driver part
The head drum control voltage (speed and phase control
information) is output via a µP-output (7899-B pin 35; PWM 14-bit).
This pulse-wide modulated signal is fed to the motor driver IC
M63100FP [7463 pin 11] and integrated with the capacitor [2469].
This IC already has a completely integrated ‘start-up’ circuit fitted.
For the commutation, the head drum motor driver uses the e.m.f.
on the non-current carrying motor coil (transformer principle). The
motor speed is also discharged from there at the same time. The
phase of the head disc is discharged from a position coil. The
speed and phase are multiplexed into one signal [7463 pin 6] and
output, which means that the falling edge of the signal is available
with a positive edge for the speed (FG/450Hz) and at 25Hz for the
position pulse (PG).
The motor driver M63100FP [7463] is connected to the head drum
motor on the motherboard using plug [1948].
•
DRUM
is the speed-phase control signal. The resolution is
14 bit.
•
PG/FG
is the combined POS/tachometer signal from the
M63100FP [7463].
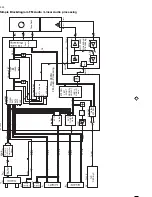
4.5 Interface to the loading motor driver part:
The loading motor driver part is constructed for use as a bridged
dual power operations amplifier (OPAMP). It can supply max. +/-
0.8A output current. The output current is limited to approx. 0.7A by
the internal resistance of the loading motor (18 Ohm typ.) (start-up
or motor is blocked).
Between the IC outputs [7463, pins 22 and 24] there is a
“Boucherot” circuit [3467] 1E, [2474] 100 nF for suppressing a
spurious 3MHz oscillation from the output stage. One half of the
bridge is controlled via the TMO line on pin 27 and acts as a
comparator. The other half is an amplifier integrator with a 3.9 gain.
A change in the input voltage (THIO) of between 0 and 5V on pin 25
results in a change in the output voltage of between 0V and almost
Ub. With 50% modulation (THIO = 2.5 V) pin 24 has approx. 7 V.
The 100nF capacitor [2473] in the negative feedback of the op-amp
filters out the PWM frequency of approx. 39kHz. During POR, the
µP issues “L” to the THIO line, whilst TMO is “H”. This ensures that
no current flows in the motor for the duration of the POR pulse. This
prevents the motor being destroyed in case of prolonged running or
blockage. This arrangement also has a disadvantage, however.
This is that if the 5 V supply fails (e.g. because the 5V fuse has
blown), residual voltages may be passed to the IC inputs via the
adjacent 14 V voltages. These residual voltages trigger the
comparator and the op-amp in opposite ways, causing a short-
circuit in the blocked loading motor after about a minute. To get
around this problem, a separate voltage divider is used internally
for the comparator. Both outputs on the M63100FP [7463] are then
in “common mode” if this error occurs.
4.6 Interface to the capstan motor
The driver IC on the capstan motor is activated via connector
[1946].
CAP is the signal for the capstan speed. This voltage may vary
without load between 0 and 5 V.
The rotational direction of the motor is determined using CREV
(capstan reverse). The maximum current input for the motor is
limited to 1A. Typical values in PLAY mode are 0.2 ... 0.3 A.
Содержание VTFX940EUKN
Страница 6: ......
Страница 30: ......
Страница 83: ...3 1 3 1 Wiring Diagram Motherboard ...
Страница 85: ...3 3 3 3 Block Diagram Video ...
Страница 87: ...3 5 3 5 Block Diagram Audio Stereo ...
Страница 88: ...3 6 3 6 Supply Voltages and Bus Diagram ...
Страница 91: ...3 9 3 9 Block Diagram Central Control AIO1 AIO2 OPTION ...
Страница 92: ...3 10 3 10 Mother Board solder side CLOCK ADJUST 4769 ...
Страница 93: ...3 11 4769 E10 ...
Страница 94: ...3 12 ...
Страница 119: ...THE UPDATED PARTS LIST FOR THIS MODEL IS AVAILABLE ON ESTA ...
Страница 120: ......