Operation Manual – MSTP
H3C S9500 Series Routing Switches
Chapter 1 MSTP Configuration
1-2
z
Configuration BPDUs, used to calculate the spanning tree and maintain the
spanning tree topology.
z
Topology change notification (TCN) BPDUs, used to notify concerned devices of
network topology changes, if any.
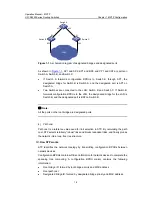
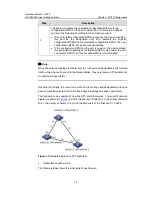
III. Basic concepts in STP
1) Root bridge
The root of a spanning tree is called the root bridge. In the entire network, there is only
one root bridge. Whichever bridge in the network can become the root bridge,
depending on the network topology.
Upon network convergence, the root bridge generates and sends out configuration
BPDUs at a certain interval and other devices just forward the BPDUs. This mechanism
ensures topological stability.
2) Root
port
In an STP network, a root port is a port on a non-root bridge device. Among the ports on
an STP-enabled device, the root port has the lowest path cost to the root bridge.
The root port takes charge of communicating with the root bridge. A non-root-bridge
device has one and only one root port. The root bridge has no root port.
3) Designated bridge and designated port
Refer to the following table for the description of designated bridge and designated
port.
Table 1-1
Description of designated bridge and designated port
Classification
Designated bridge
Designated port
For a device
The device directly connected
with this device and responsible
for forwarding configuration
BPDUs
The port through which the
designated bridge forwards
configuration BPDUs to this
device
For a LAN
The device responsible for
forwarding configuration BPDUs
to this LAN segment
The port through which the
designated bridge forwards
configuration BPDUs to this
LAN segment