220
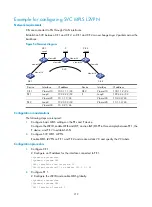
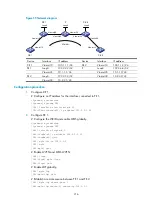
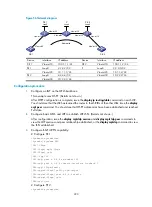
Figure 56
Network diagram
Device Interface IP
address
Device
Interface
IP address
CE 1
Vlan-int10
100.1.1.1/24
CE 2
Vlan-int10 100.1.1.2/24
PE 1
Loop0
2.2.2.2/32
P
Loop0
3.3.3.3/32
Vlan-int20
10.1.1.1/24
Vlan-int20 10.1.1.2/24
PE 2
Loop0
4.4.4.4/32
Vlan-int30 10.2.2.2/24
Vlan-int30
10.2.2.1/24
Configuration procedure
1.
Configure an IGP on the MPLS backbone.
This example uses OSPF. (Details not shown.)
After OSPF configuration is complete, issue the
display ip routing-table
command on each LSR.
You should see that the LSR has learned the routes to the LSR IDs of the other LSRs. Issue the
display
ospf peer
command. You should see that OSPF adjacencies have been established and reached
Full state.
2.
Configure basic MPLS and LDP to establish LDP LSPs. (Details not shown.)
After configuration, issue the
display mpls ldp session
and
display mpls ldp peer
commands to
view the LDP sessions and peer relationship established, or the
display mpls lsp
command to view
the LSPs established.
3.
Configure BGP L2VPN capability:
# Configure PE 1.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] sysname PE1
[PE1] l2vpn
[PE1-l2vpn] mpls l2vpn
[PE1-l2vpn] quit
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp] peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp] peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp] l2vpn-family
[PE1-bgp-af-l2vpn] policy vpn-target
[PE1-bgp-af-l2vpn] peer 4.4.4.4 enable
[PE1-bgp-af-l2vpn] quit
[PE1-bgp] quit
# Configure PE 2.
<Sysname> system-view
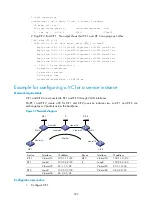
Vlan-int20
Vlan-int20
Loop0
Vlan-int30
Vlan-int30
Vlan-int10
Vlan-int10
Vlan-int10
Vlan-int10
Loop0
Loop0
PE 1
PE 2
P
CE 1
CE 2
Kompella