134
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] quit
[SwitchB] interface loopback 0
[SwitchB-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[SwitchB-LoopBack0] isis circuit-level level-2
[SwitchB-LoopBack0] quit
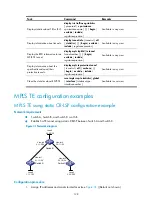
# Configure Switch C.
<SwitchC> system-view
[SwitchC] isis 1
[SwitchC-isis-1] network-entity 00.0005.0000.0000.0003.00
[SwitchC-isis-1] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 3
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface3] isis enable 1
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface3] isis circuit-level level-2
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface3] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 2
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface2] isis enable 1
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface2] isis circuit-level level-2
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface2] quit
[SwitchC] interface loopback 0
[SwitchC-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[SwitchC-LoopBack0] isis circuit-level level-2
[SwitchC-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure Switch D.
<SwitchD> system-view
[SwitchD] isis 1
[SwitchD-isis-1] network-entity 00.0005.0000.0000.0004.00
[SwitchD-isis-1] quit
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 3
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface3] isis enable 1
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface3] isis circuit-level level-2
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface3] quit
[SwitchD] interface loopback 0
[SwitchD-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[SwitchD-LoopBack0] isis circuit-level level-2
[SwitchD-LoopBack0] quit
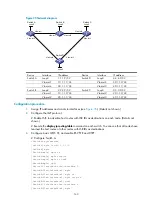
Execute the
display ip routing-table
command on each switch. The output shows that all nodes
have learned the host routes of other nodes with LSR IDs as destinations. Take Switch A for
example:
[SwitchA] display ip routing-table
Routing Tables: Public
Destinations : 10 Routes : 10
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
1.1.1.9/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
2.2.2.9/32 ISIS 15 10 10.1.1.2 Vlan1
3.3.3.9/32 ISIS 15 20 10.1.1.2 Vlan1
4.4.4.9/32 ISIS 15 30 10.1.1.2 Vlan1
10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.1 Vlan1
10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0