-3
-
2.3 Arc Welding Sequence
The steel surface is cleaned using a wire brush to remove all scale, rust, dirt and oil. The
blocks are then removed from the spacing jig and pressed firmly against the steel surface
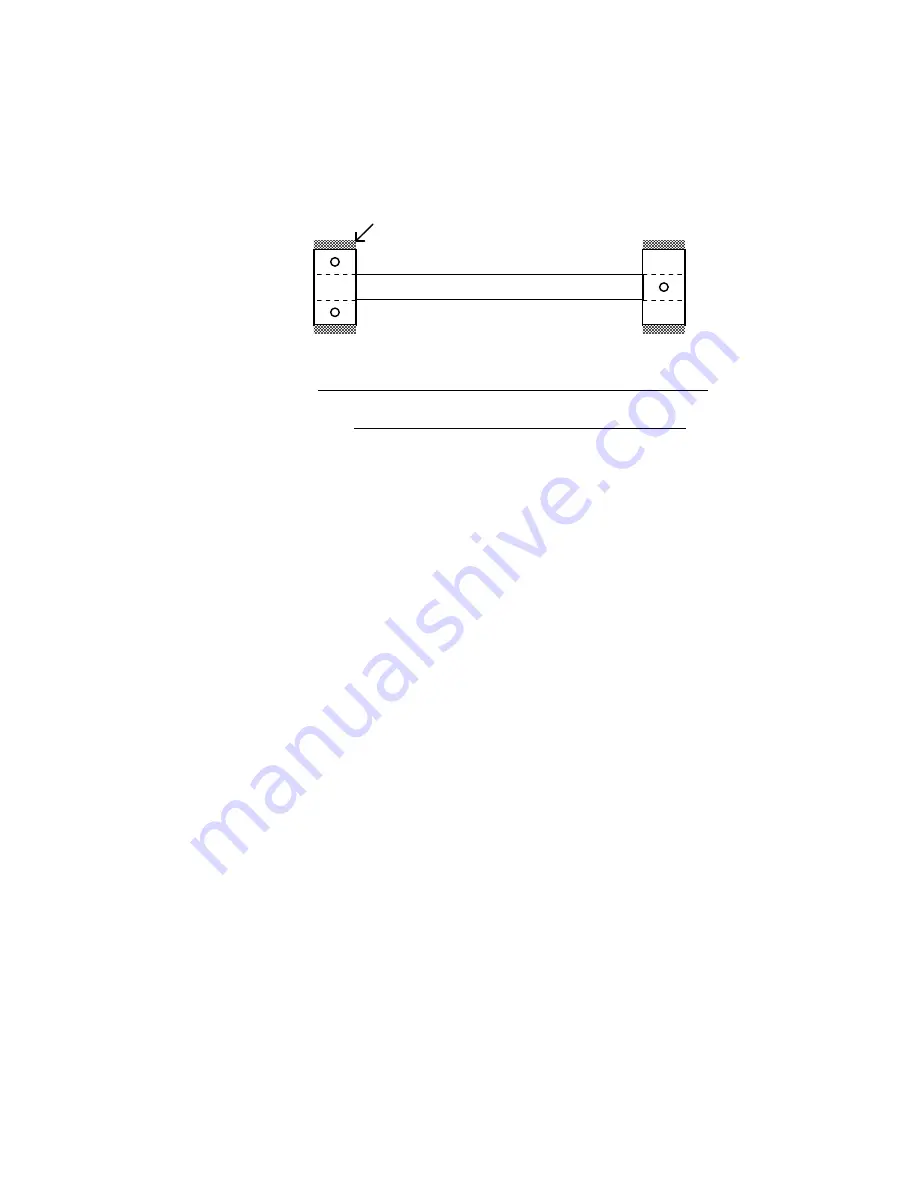
using the spacer bar as a handle. The edges of the mounting blocks are now welded in the
order as shown in Figure 3.
1
3
4
2
SPACER BAR
WELD
Figure 3 - Welding Sequence for the Mounting Blocks
Avoid excessive heat and DO NOT WELD THE FLAT END SURFACES as this will prevent
removal of the spacer bar. Avoid welding splatter which could stick to the spacer bar.
To
speed things up, where many gages are being installed, it is advantageous to have
more than one spacer bar.
After welding, cool the mounting blocks with a water-soaked rag, then slacken the set
screws and slide out the spacer bar. Clean away all welding slag using a chipping hammer
and wire brush. (Optional: Paint over the surface to provide some protection against
corrosion).
2.4 Setting the Strain Gage
When the mounting blocks have been welded in place the strain gage can be slid into the
holes in the mounting blocks. One end of the strain gage has a V-groove in it - make sure
that this end goes inside the mounting block that has the single cone-point set screw.
Tighten hard the cone point set screw into the V-groove. Now clip the coil housing around
the gage and connect to the readout box (
Channel C
). Set the initial reading on the gage to
the correct level depending on whether compressive or tensile strains are anticipated. The
useable range of the strain gage runs from around 1000 to 4000 microstrains. The mid-
range reading is 2500. The reading can be adjusted by simply pulling or pushing on the free
end of the strain gage. Strain gages are shipped with a reading of around 3000 to 3500.
This level is OK for compressive strains. If tensile strains are to be measured set the initial
reading to around 1500.
When the desired reading has been achieved tighten the two cone-point set screws in the
mounting block: tighten hard down onto the end of the strain gage. Tighten the hose clamp
onto the coil housing: tighten hard using a nut driver.
Finish off by tapping the mounting
blocks with, say, the handle of a screwdriver, to remove any installation strains and
stabilize the initial reading. Tap until the reading remains stable










































