Getting started
Planning the FortiGate configuration
FortiGate-1000 Installation Guide
01-28004-0025-20040830
21
NAT/Route mode
In NAT/Route mode, the FortiGate unit is visible to the network. Like a router, all its
interfaces are on different subnets. The following interfaces are available in
NAT/Route mode:
• External is the interface to the external network (usually the Internet).
• Internal is the interface to the internal network.
• Ports 1 and 3 can be connected to any networks.
• Port 2 can be connected to a DMZ network or to any other network.
• Port 4/HA can be connected to another network. Port 4/HA can also be connected
to other FortiGate-1000 units if you are installing an HA cluster.
You can add firewall policies to control whether communications through the
FortiGate unit operate in NAT or Route mode. Firewall policies control the flow of
traffic based on the source address, destination address, and service of each packet.
In NAT mode, the FortiGate unit performs network address translation before it sends
the packet to the destination network. In Route mode, there is no address translation.
You typically use NAT/Route mode when the FortiGate unit is operating as a gateway
between private and public networks. In this configuration, you would create NAT
mode firewall policies to control traffic flowing between the internal, private network
and the external, public network (usually the Internet).
If you have multiple internal networks, such as a DMZ network in addition to the
internal, private network, you could create route mode firewall policies for traffic
flowing between them.
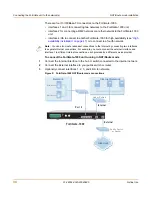
Figure 5: Example NAT/Route mode network configuration
NAT/Route mode with multiple external network connections
In NAT/Route mode, you can configure the FortiGate unit with multiple redundant
connections to the external network (usually the Internet). For example, you could
create the following configuration:
• External is the default interface to the external network (usually the Internet).
• Port 1 is the redundant interface to the external network.
• Internal is the interface to the internal network.
• Port 2 is the interface to the DMZ network.
FortiGate-1000 Unit
in NAT/Route mode
Route mode policies
controlling traffic between
internal networks.
Internal network
DMZ network
Internal
192.168.1.1
Port 2
10.10.10.2
192.168.1.3
10.10.10.23
External
204.23.1.5
NAT mode policies controlling
traffic between internal and
external networks.
Internet
6
7
8
Esc
Enter
INTERNAL
EXTERNAL
1
2
3
4 / HA