9
Proximity Pilot (PP) State (Cable Simulation)
To simulate various current capabilities of the charging cable, connect the
test adapter to the charging station and set the PP State rotary switch (item
1
,
Figure 2). The adapter simulates the current capabilities with different
resistances connected between PP and PE conductors. See Table 2 for the
correlation between resistance and current capability of the charging cable.
Note
If the charging station has a fixed cable with vehicle connector then
this setting of PP is not used in all.
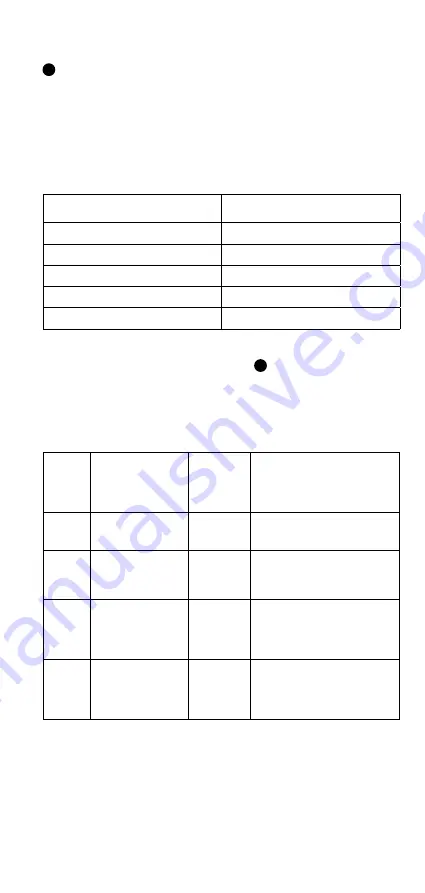
Table 2. Correlation between resistance and current capability of
the charging cable.
Marking of cable current
capability
Resistance between PP and PE
No cable
Open (
∞
)
13 A
1.5 kΩ
20 A
680 Ω
32 A
220 Ω
63 A
100 Ω
Control Pilot (CP) State (Vehicle Simulation)
Use the CP State rotary switch selector (item
10
, Figure 2), to simulate
various vehicle states when the test adapter is connected to the charging
station. Vehicle states are simulated with different resistances connected
between CP and PE conductors. Correlation between resistance and vehicle
states is shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Correlation between resistance, vehicle state and CP voltage signal.
Marking
of
Vehicle
State
Electric Vehicle
(EV) State
Resistance
between
CP and PE
Voltage at CP terminal
A
Electric vehicle
(EV) not
connected
Open (
∞
)
A1: +12 V
or
A2: ±12 V PWM (1 kHz)
B
Electric vehicle
(EV) connected,
not ready to
charge
2.74 kΩ
B1: +9 V
or
B2: +9 V / -12 V PWM (1 kHz)
C
Electric vehicle
(EV) connected,
ventilation not
required, ready
to charge
882 Ω
C1: +6 V
or
C2: +6 V / -12 V PWM (1 kHz)
D
Electric vehicle
(EV) connected,
ventilation
required, ready
to charge
246 Ω
D1: +3 V
or
D2: +3 V / -12 V PWM (1 kHz)

































