ERPN-M USER INSTRUCTIONS ENGLISH 02-08
Page 14 of 37
3.3.3.3 Semi open impeller
The pump casing is equipped with a renewable wear
plate.The axial thrust is balanced by back vanes.
3.3.3.4 Inducer
All different impellers can be optionally equipped with
an inducer for low NPSHA applications.
3.3.4 Magnetic Coupling
The magnetic coupling consists of:
a) The
Can:
This is the actual sealing element of the magnetic
coupling. The driving torque is transmitted via the
can due to the magnetic field between the inner
and outer rotors.
b) Outer
Rotor:
The outer rotor driven by the pump shaft and
holds the set of magnets needed to meet the
torque requirement.
c) Inner
Rotor:
The inner rotor drives the impeller. Fluid
lubricated Silicon Carbide bearings take all the
hydraulic forces.
d) Secondary
Seal:
As required by API 685 a secondary seal is used
to avoid leakage to the atmosphere in case of
magnetic coupling failure.
e) Temperature
Sensor:
It observes the temperature at the Can surface to
ensure that the Silicon Carbide bearings are
flushed properly.
3.4 Performance and operating limits
In the interest of operator safety
the unit must not be operated above the nameplate
conditions. Such operation could result in unit failure
causing injury to operating personnel. Consult
instruction book for correct operation and
maintenance of the pump and its supporting
components.
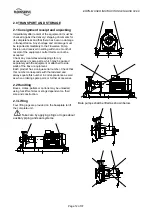
4.0 INSTALLATION
Equipment operated in hazardous locations
must comply with the relevant explosion protection
regulations, see section 1.6.4,
Products used in
potentially explosive atmospheres.
4.1 Location
The pump should be located to allow room for
access, ventilation, maintenance and inspection with
ample headroom for lifting and should be as close as
practicable to the supply of liquid to be pumped.
Refer to the general arrangement drawing for the
pump set.
4.2 Part Assemblies
The pumps are delivered completely mounted and
prealigned with the motor. Also the shaft seal is in the
correct position. Final alignment after complete
installation is necessary. If drivers and/or seal systems
are delivered separately, follow the assembly
procedure in section 6.8.
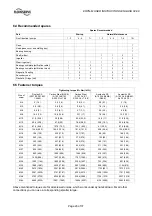
4.3 Foundation
The foundation shall be located on a place that allows
a minimum of pipe work and that is easily accessible
for inspection during operation. According to the
environment the foundation may consist of concrete
or of steel. It must be rigid and heavy enough to
absorb normal vibrations and shocks.
4.3.1 Horizontal alignment of the baseplate
Horizontal alignment is done with levelling screws.
Use a spirit level for correct horizontal alignment of
the baseplate.
The max. misalignment is 0.5 mm/m
baseplate length.
4.3.2 Steel foundation
When the pump unit is mounted directly on structural
steel frame, it shall be well supported by constructural
beams. It is recommended to check the natural
frequency of the steel frame, because it shall not
coincide with the pump speed. The exact horizontal
alignment is very important!
Ensure that the base plate is
leveled horizontally to 0.5 mm/m. To avoid any
distortion of put shims under the base plate before
bolting it down to the steel frame. Welding of the base
plate to the steel frame is not recommended because
of possible distortion of the same.
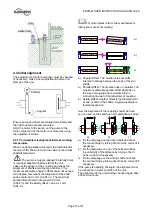
4.3.3 Concrete foundation
A concrete foundation must have an exact horizontal
alignment and must be placed on solid ground. First a
basic foundation shall be built with square shaped
holes for embedding the foundation bolts. After
putting the base plate into the foundation the proper
alignment can be obtained by adjusting it with shims
under the base plate. Now insert the foundation bolts
and grout the space between the basic foundation
and the base plate with grouting cement (refer to
illustration)
It is very helpful to use a properly made and stable
wooden frame around the base plate. So the grouting
cement will not flow side. When the grouting is totally
set and hardened the foundation bolts shall be
tightened in a firm and symmetrical way.