5 INTERRUPT CONTROLLER (ITC)
S1C17M20/M21/M22/M23/M24/M25
Seiko Epson Corporation
5-3
TECHNICAL MANUAL (Rev. 1.0)
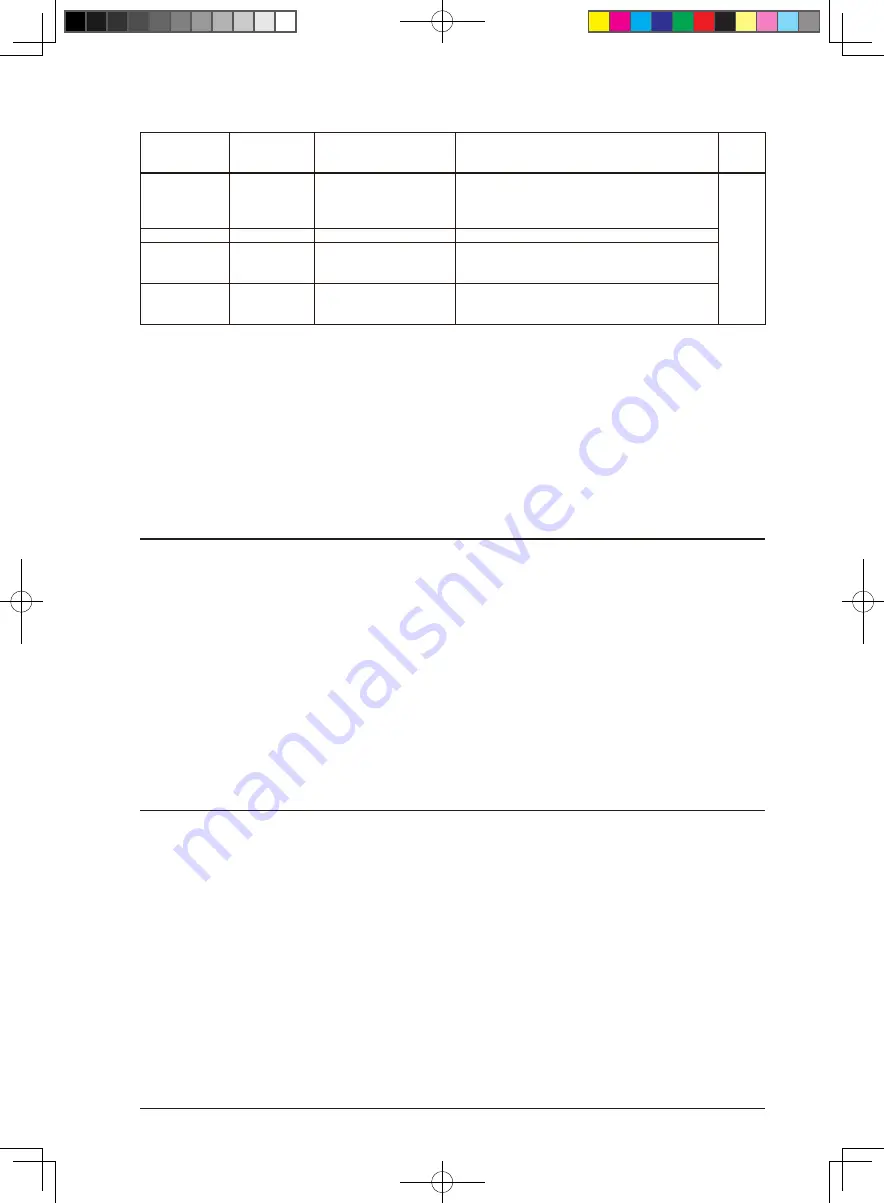
Vector number/
Software interrupt
number
Vector address Hardware interrupt name
Hardware interrupt flag
Priority
23 (0x17)
TTBR + 0x5c Synchronous serial interface
Ch.1 interrupt
• End of transmission
• Receive buffer full
• Transmit buffer empty
• Overrun error
24 (0x18)
TTBR + 0x60 16-bit timer Ch.3 interrupt
Underflow
25 (0x19)
TTBR + 0x64 12-bit A/D converter
interrupt
• Analog input signal m A/D conversion completion
• Analog input signal m A/D conversion result over-
write error
26 (0x1a)
TTBR + 0x68
reserved
–
:
:
:
:
↓
31 (0x1f)
TTBR + 0x7c
reserved
–
Low
*
1
*
1 When the same interrupt level is set
*
2 Either reset or NMI can be selected as the watchdog timer interrupt with software.
5.2.1 Vector Table Base Address (TTBR)
The MSCTTBRL and MSCTTBRH registers are provided to set the base (start) address of the vector table in which
interrupt vectors are programmed. “TTBR” described in Table 5.2.1 means the value set to these registers. After an
initial reset, the MSCTTBRL and MSCTTBRH registers are set to address 0x8000. Therefore, even when the vec-
tor table location is changed, it is necessary that at least the reset vector be written to the above address. Bits 7 to 0
in the MSCTTBRL register are fixed at 0, so the vector table always begins from a 256-byte boundary address.
5.3 Initialization
The following shows an example of the initial setting procedure related to interrupts:
1. Execute the di instruction to set the CPU into interrupt disabled state.
2. If the vector table start address is different from the default address, set it to the MSCTTBRL and MSCTTBRH
registers after removing system protection by writing 0x0096 to the MSCPROT.PROT[15:0] bits. Then, write a
value other than 0x0096 to the MSCPROT.PROT[15:0] bits to set system protection.
3. Set the interrupt enable bit of the peripheral circuit to 0 (interrupt disabled).
4. Set the interrupt level for the peripheral circuit using the ITCLV
x
.ILV
x
[2:0] bits in the ITC.
5. Configure the peripheral circuit and start its operation.
6. Clear the interrupt factor flag of the peripheral circuit.
7. Set the interrupt enable bit of the peripheral circuit to 1 (interrupt enabled).
8. Execute the ei instruction to set the CPU into interrupt enabled state.
5.4 Maskable Interrupt Control and Operations
5.4.1 Peripheral Circuit Interrupt Control
The peripheral circuit that generates interrupts includes an interrupt enable bit and an interrupt flag for each inter-
rupt cause.
Interrupt flag:
The flag is set to 1 when the interrupt cause occurs. The clear condition depends on the periph-
eral circuit.
Interrupt enable bit: By setting this bit to 1 (interrupt enabled), an interrupt request will be sent to the ITC when the
interrupt flag is set to 1. When this bit is set to 0 (interrupt disabled), no interrupt request will
be sent to the ITC even if the interrupt flag is set to 1. An interrupt request is also sent to the
ITC if the status is changed to interrupt enabled when the interrupt flag is 1.
For specific information on causes of interrupts, interrupt flags, and interrupt enable bits, refer to the respective pe-
ripheral circuit descriptions.
Note: To prevent occurrence of unnecessary interrupts, the corresponding interrupt flag should be
cleared before setting the interrupt enable bit to 1 (interrupt enabled) and before terminating the
interrupt handler routine.
















































