7
50 (3.45)
1 (1.4)
1 (1.4)
2 (2.7)
2 (2.7)
100 (6.89)
2 (2.7)
3 (4.1)
4 (5.4)
4 (5.4)
150 (10.34)
2 (2.7)
4 (5.4)
5 (6.8)
6 (8.1)
200 (13.79)
3 (4.1)
5 (6.8)
7 (9.5)
8 (10.8)
250 (17.24)
4 (5.4)
6 (8.1)
9 (12.2)
10 (13.6)
300 (20.68)
5 (6.8)
7 (9.5)
11 (14.9)
12 (16.3)
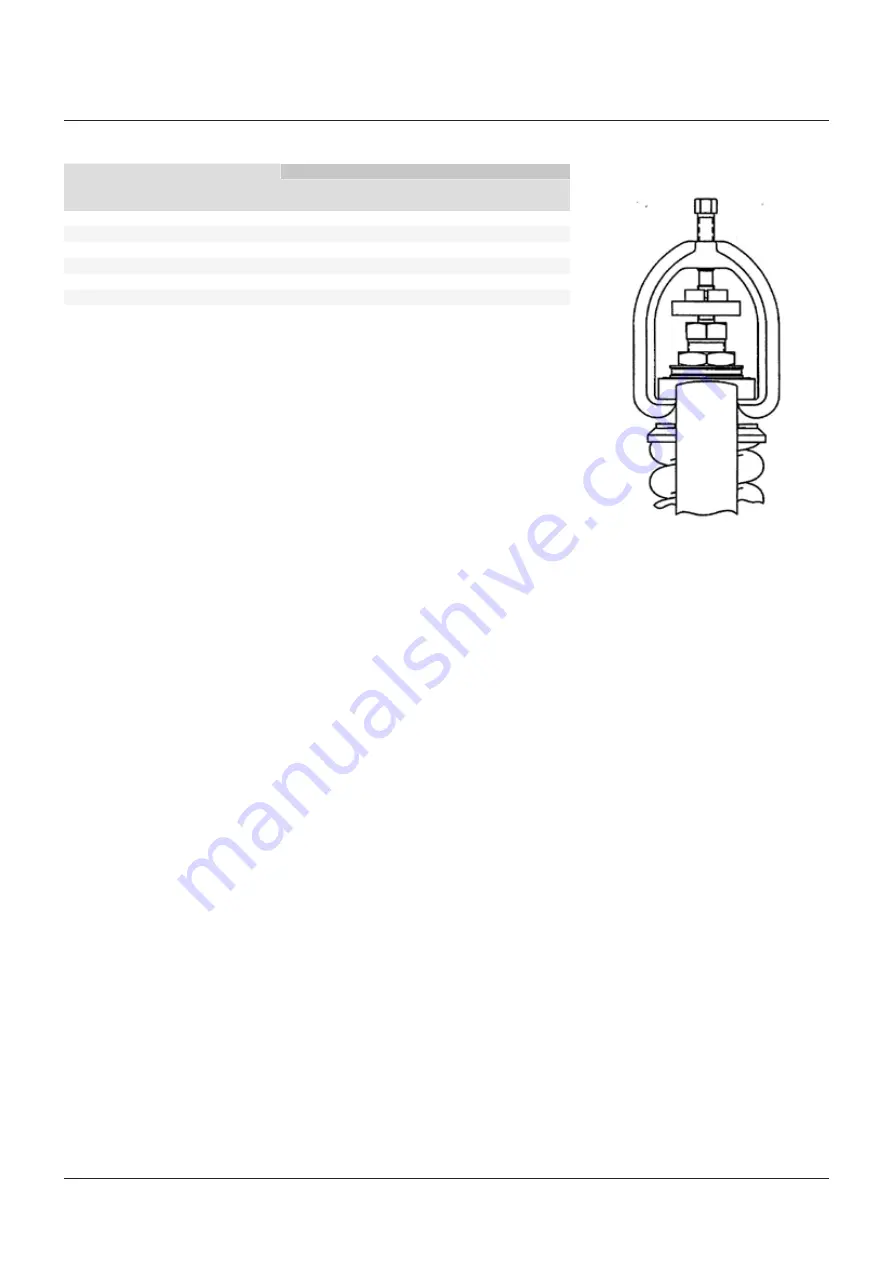
Hydrostatic test using gag
The safety valve test gag shown in Figure 5 can
be used with both welded and flanged inlets,
but at pressures no greater than 10% above the
nameplate set pressure.
Gagging should be done very carefully in
order not to overload the valve spindle or
cause damage to the valve seats.
The following outlines the recommended
procedure for gagging valves for
hydrostatic test:
• Remove the lever (27), forked lever (30),
cap (25) and spindle nut (23).
• Refer to Figure 5. Lubricate the threads and
pointed end of the gag screw. Install the
gag in place, being careful that the legs fit
uniformly. Contacts on both legs of the gag
should seat evenly on the underside of the
bonnet top.
• Tighten the gag finger-tight only at this point.
• Raise the system pressure to approximately
100 psig below the nameplate set pressure
of the safety valve.
• Apply the necessary torque to the gag in
accordance with the value shown in the
table above for the specific orifice size. This
torque value is determined as follows:
- Determine Δ by subtracting the valve set
pressure from the hydrostatic test pressure.
- Read the value of Δ on the vertical scale.
Proceed horizontally to the appropriate
orifice size and then down to read the
torque on the horizontal scale.
- The torque values (foot-pounds) obtained
should be increased by a factor of
approximately 25% to account for normal
variations in friction, safety valves and
test conditions.
CAUTION
Gags should not be used when inlet pressures are
more than 10% greater than the safety valve set
pressure. Damage to the valve may result.
CAUTION
Should any safety valve show seat leakage, the
pressure must be lowered until the leakage stops.
CAUTION
Never increase the gagging load while a safety
valve shows seat leakage. This can result
in damage to the valve seats and bending
of the spindle.
CAUTION
Valve gags should not be left on the valves in
a gagged or loaded position for an extended
period or under conditions where large thermal
variations are expected.
FIGURE 5 - VALVE GAG
POSITION GAG EVENLY ON BONNET
• The torque should then be increased on the
gag about 10% above the initial torque value.
• After the hydrostatic test, the pressure on the
system should be dropped to approximately
100 psi below the nameplate set pressure of
the safety valve. The gags should be loosened
at this point and removed from the valves.
• After the hydrostatic test, the gag should be
removed and the cap reinstalled according
to Section 10 - paragraph 'Assembly of cap'.
NORMAL GAGGING LOAD in ft·lb OF TORQUE (Nm) VS. ΔP
ΔP
Orifice
(Overpressure less valve set pressure)
psi (bar)
psi (bar)
K
K
2
M
M
2
CROSBY
®
STYLES HC AND HCA ISOFLEX™ SAFETY VALVES
INSTALLATION, MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENT INSTRUCTIONS
• After applying the necessary torque to the
gags, increase the hydrostatic test pressure
to the required amount. Observations should
be made during the rising pressure cycle to
determine if any of the safety valves show
seat leakage.



















