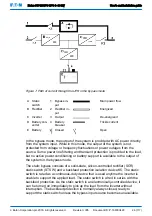
Figure 6. Path of current through the UPS in the battery mode
A Static
switch
1 Bypass in-
put
Main power flow
B Rectifier
2 Rectifier in-
put
Energized
C Inverter
3 Output
De-energized
D Battery con-
verter
4 Battery
breaker
Trickle current
E Battery
Closed
Open
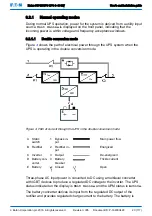
During a utility power failure, the rectifier no longer has an AC utility source from
which to supply the DC output current required to support the inverter. The input
relay K1 opens and the UPS output is powered from the batteries through the
inverter. As the inverter operates uninterrupted through the transition, the load
remains supported continuously without disturbance. If the UPS static bypass is
supplied from the same source as the UPS rectifier, the backfeed protection
contactor K5 also opens. The opening of K1 and K5 prevent system voltages
from bleeding backwards and re-entering the input source through the static
switch or rectifier.
If the input power fails to return or is not within the acceptance windows required
for normal operation, the battery continues discharging until a DC voltage level
is reached where the inverter output can no longer support the connected loads.
The UPS issues a Low Battery alarm to indicate that the battery voltage level is
running low. The UPS continues to discharge the batteries until the battery
voltage reaches the threshold level of the Low Battery alarm. If the bypass is
Eaton 91PS/93PS UPS 8–40 kW
User's and installation guide
©
Eaton Corporation plc 2018. All rights reserved.
Revision: 005
Document ID: P-164000493
24 (117)