8.
CR #24~ CR #27: means analog input voltage or current when conversion value from analog
signal to digital is 4000. Voltage setting range: -4V~+20V(-3200
LSB
~+16000
LSB
). Current setting
range: -16mA~+52mA(-3200
LSB
~+10400
LSB
). But it needs to notice that GAIN VALUE –
OFFSET VALUE = +800
LSB
~+12000
LSB
(voltage) or +800
LSB
~+6400
LSB
(current). When this
value under this range, the resolution of the input signal will be thin and the variation of value
will be larger. When this value exceeds this range, the resolution of input signal will be thick
and the variation of value will be smaller.
9.
CR#30 is fault code. Please refer to the following chart.
Fault
description
Content b15~b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
Power
source
abnormal K1(H1)
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Analog
input
value
error K2(H2)
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
Setting
mode
error
K4(H4)
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
Offset/Gain
error
K8(H8)
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
Hardware
malfunction
K16(H10)
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
Digital
range
error
K32(H20)
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
Average
times
setting
error
K64(H40)
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
Command error
K128(H80)
Reserved
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Note: Each fault code will have corresponding bit (b0~b7). Two or more faults may happen at the same time.
0 means normal and 1 means having fault.
10. CR#31: it is used to set RS-485 communication address. Setting range is 01~255 and factory
setting is K1.
11. CR#32 is used to set RS-485 communication baud rate: 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200
bps. b0: 4800bps. b1: 9600bps. (factory setting) b2: 19200bps. b3: 38400 bps. b4: 57600 bps. b5:
115200 bps. b6-b13: reserved. b14: exchange low and high byte of CRC check code. (only for RTU
mode) b15=0: ASCII mode. b15=1: RTU mode.
12. CR#33 is used to set the inner function priority. For example: characteristic register. Output
latched function will save output setting in the inner memory before loss power.
13. CR#34: software version.
14. CR#35~ CR#48: system used.
15. The corresponding parameters address H4000~H4030 of CR#0~CR#48 can provide user to
read/write data by RS-485.
A. Communication baud rate: 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200 bps.
B. Communication format: ASCII mode is 7Bit, even bit, 1 stop bit (7 E 1). Communication
format of RTU mode is 8Bit, even bit, 1 stop bit (8 E 1).
C. Function code: 03H—read data from register. 06H—write a WORD into register. 10H—write
many WORDs into register.
5
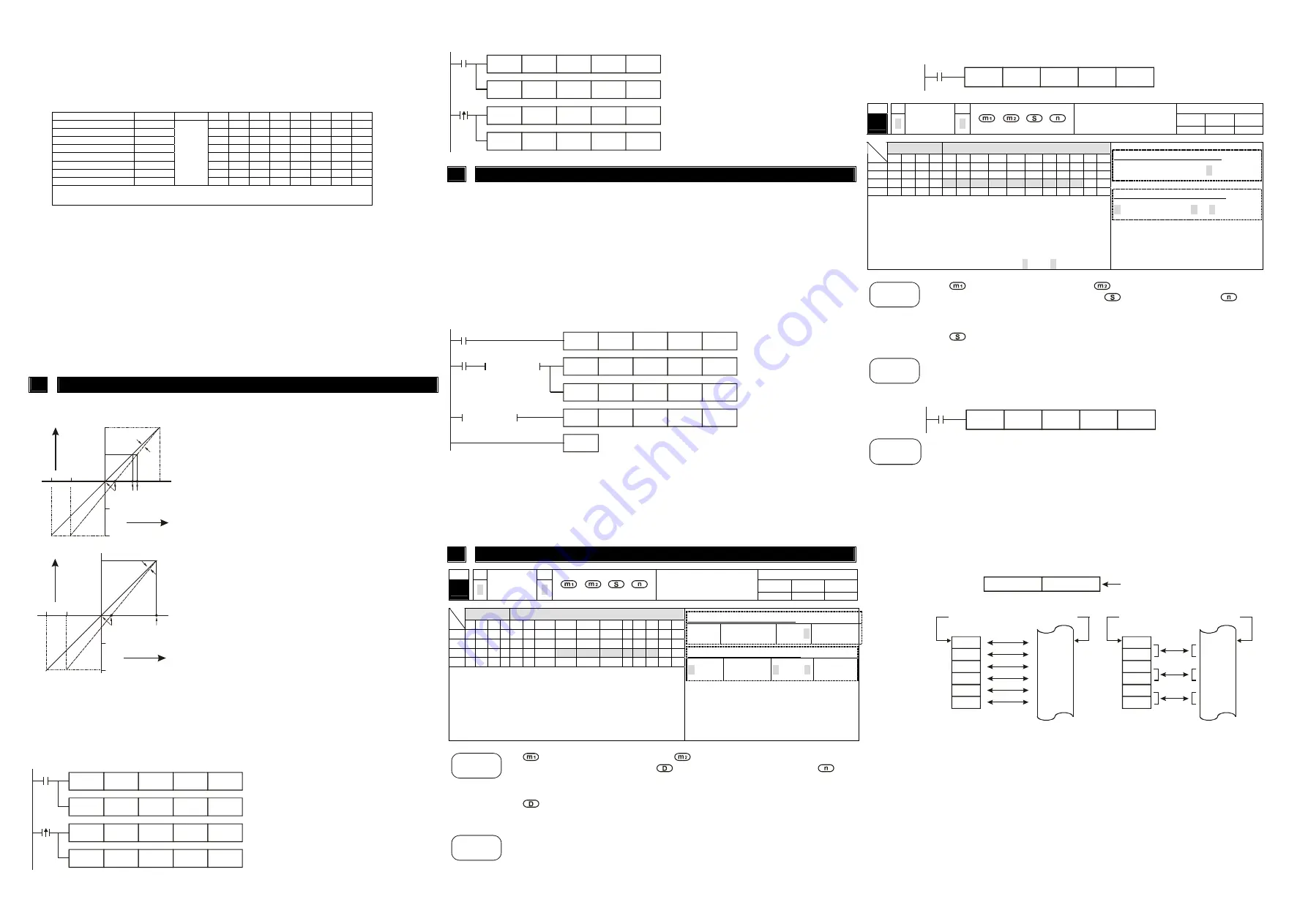
Adjust A/D Conversion Characteristic Curve
5.1 Adjust A/D Conversion Characteristic Curve
Voltage input mode
Mode 0 of CR#1 GAIN=5V(4000
LSB
), OFFSET=0V (0
LSB
)
Mode 1 of CR#1 GAIN=6V(4800
LSB
), OFFSET=2V (1600
LSB
)
GAIN:
Voltage input value when digital output is
4000. Setting range is -4V~+20V(-3200
LSB
~
+16000
LSB
)
OFFSET:
Voltage input value when digital output is 0.
Setting range: -5V~+5V(-4000
LSB
~
+4000
LSB
)
+8000
+4000
-4000
10V
-8000
-6V
-10V
6V
5V
2V
0
GAIN
OFFSET
Digital
output
Mode 0
Mode 1
Voltage input
GAIN
-
OFFSET: Setting range is +1V~+15V (+800
LSB
~
+12000
LSB
)
Current input mode
Mode 2 of CR#1: GAIN = 20mA(4000
LSB
), OFFSET=4mA
(800
LSB
).
Mode 3 of CR#1: GAIN = 20mA(4000
LSB
), OFFSET=0mA
(0
LSB
).
GAIN:
Current input value when digital output is
+4000. Setting range is -20 mA~+20 mA
(-4000
LSB
~ +4000
LSB
)
OFFSET:
Current input value when digital output
value is 0. Setting range is-16 mA ~+52 mA
(-3200
LSB
~ +10400
LSB
)
+4000
-4000
-12mA
-20mA
4mA
0
OFFSET
20mA
GAIN
Digital
output
Mode 3
Mode 2
Current input
GAIN
-
OFFSET: Setting range is +4mA ~ +32mA (800
LSB
~
+6400
LSB
)
The chart above is to adjust A/D conversion characteristic curve of voltage input mode and
current input mode. Users can adjust conversion characteristic curve by changing OFFSET values
(CR#18~CR#21) and GAIN values (CR#24~CR#27) depend on application.
LSB(Least Significant Bit): 1. voltage input: 1
LSB
=10V/8000=1.25mV. 2. current input:
1
LSB
=20mA/4000=5µA.
5.2. Program Example for Adjusting A/D Conversion Characteristics Curve
Example 1: setting OFFSET value of CH1 to 0V(=K0
LSB
) and GAIN value of CH1 to 2.5V(=K2000
LSB
).
X0
K2000
K24
H0
K1
K0
K1
H0
K1
M1002
K0
K33
K1
K0
K1
K18
K0
K0
TO
TO
TO
TO
Writing H0 to CR#1 of analog input
module no. 0 and set CH1 to mode 0
(voltage input -10V~+10V)
Writing H1 to CR#33 and allow to
adjust characters of CH1.
When X0 switches from OFF to ON,
K0
LSB
of
OFFSET value will be wrote in
CR#18 and K2000
LSB
of GAIN value
will be wrote in CR#24.
Example 2: setting OFFSET value of CH2 to 2mA(=K400
LSB
) and GAIN value of CH2 to 18 mA
(=K3600
LSB
)
X0
K1
K0
K1
H0
K1
M1002
K0
K33
K1
K0
K1
K0
H18
K19
K25
K400
K3600
TO
TO
TO
TO
Writing H18 to CR#1 of analog input mode
no. 0 and set CH2 to mode 3 (current input:
-20 mA ~ +20mA)
Writing H0 to CR#33 and allow to adjust
characteristics of CH4.
When X0 switches from OFF to ON,
K400
LSB
of
OFFSET value will be wrote in
CR#19 and K3600
LSB
of GAIN value will be
wrote in CR#25.
6
Initial PLC Start-up
Lamp display:
1.
When power is on, POWER LED will be lit and ERROR LED will be lit for 0.5 second.
2.
When it is normal that POWER LED should be lit and ERROR LED should turn off. When
power supply is lower than 19.5V, ERROR LED will blink continuously till the power supply
is higher than 19.5V.
3.
When it connects to PLC MPU in series, RUN LED on MPU will be lit and A/D LED or D/A
LED should blink.
4.
After receiving the first RS-485 command during controlling by RS-485, A/D LED or D/A
LED should blink.
5.
After converting, ERROR LED should blink if input or output exceeds upper bound or lower
than lower bound.
Example:
K1
K0
K1
K1
K0
K0
K0
M1000
FROM
TO
END
K2
K6
D0
H3030
K32
D20
K4
FROM
TO
K0
K2
= H88 D0
M1002
= H88 D0
Explanation:
Reading the data of model type from expansion module K0 and distinguish if the data is H88
(DVP04AD-S model type).
If the model type is DVP04AD-S, M11 is on and the setting input mode is (CH1, CH3)= mode 0,
(CH2, CH4)= mode 3.
Setting the average times of CH1 and CH2 are K32.
Reading the input signal average value of CH1~CH4 (4 data) saving in D20~D23.
7
Related Instructions Explanation
API
Adaptive model
ES EP EH
78
D
FROM
P
Special module CR
data read out
Bit device
Word device
X Y M S K H KnX KnY KnM KnS T C D E F
m
1
¼
¼
m
2
¼
¼
D
¼
¼
¼
¼ ¼ ¼ ¼
¼
n
¼
¼
Note: The usage range of operand m
1
is 0~7.
The usage range of operand m
2
: ES/EP:
0-48, EH: 0-254.
The usage range of operand n: ES/EP: n=
1~(49-m2), EH: 1~(255-m2).
ES series model doesn’t support pulse
execution command (FROMP, DFROMP).
16-bit command (9 STEPS)
FROM
Continuous
execution
FROMP
Pulse
execution
32-bit command (17 STEPS)
DFROM
Continuous
execution
DFROMP
Pulse
execution
Flag: When M1083=On, it allows to
insert interrupt during
FROM/TO.
Refer to following for detail.
Command
Explanation
: the number for special module.
: the number of CR (Control Register) of
special module that will be read.
: the location to save reading data.
: the
data number of reading one time.
DVP-series PLC uses this command to read CR data of special module.
: When assigning bit operand, K1~K4 can be used for 16-bit and K5~K8 can be
used for 32-bit.
Please refer the following footnote for calculating of special module number.
Program
Example
To read the content of CR#24 of special module#0 to D0 of PLC and to read the
content of CR#25 of special module#0 to D1 of PLC. It can read 2 data in one time
(n=2).
The command will be executed when X0=ON. The command won’t be executed
when X0=OFF and the content of previous reading data won’t change.
X0
FROM
K0
K24
D0
K2
API
Adaptive model
ES
EP
EH
79
D
TO
P
Special module CR
data write in
Bit device
Word device
X
Y
M S K H KnX KnY KnM KnS T C D E
F
m
1
¼
¼
m
2
¼
¼
S
¼
¼
¼
¼
¼
¼
¼
¼
¼
¼
¼
n
¼
¼
Note: The usage range of operand m
1
is 0~7.
The usage range of operand m
2
: ES/EP: 0-48,
EH: 0-254.
The usa ge range of operand n: ES/EP: n=
1~(49-m2), EH: 1~(255-m2).
For ES series, it doesn’t support pulse
execution command (TOP, DTOP)
16-bit command (9 STEPS)
TO
Continuous
execution
TOP
Pulse
execution
32-bit command (17 STEPS)
DTO
Continuous
execution
DTOP
Pulse
execution
Flag: When M1083=On, it allows
to insert interrupt during
FROM/TO.
Refer to following for detail.
Command
Explanation
: the number of special module.
: the number of CR (Control Register)
of special module that will be wrote in.
: the data to write in CR.
: the
data number to write in one time.
DVP-series PLC uses this command to write data into CR of special module.
: When assigning bit operand, K1~K4 can be used for 16-bit and K5~K8 can
be used for 32-bit.
Program
Example
Using 32-bit command DTO, program will write D11 and D10 into CR#3 and CR#2
of special module#0. It only writes a group of data in one time (n=1).
The command will be executed when X0=ON and it won’t be executed when
X0=OFF. The data that wrote in previous won’t have any change.
X0
K0
K2
D0
DTO
K1
Footnote
The rule of command operand:
m1: arrangement number of special module. The number of special module
that connects to PLC MPU. The numbering order of special module from the
near to the distant of MPU is from 0 to 7. The maximum is 8 special modules
and won’t occupy I/O point.
m2: the number of CR. Built in 16-bit of 49 groups memory of special module
is called CR (Control Register). The number of CR uses decimal digital
(#0~#48). All running status and setting values of special module has
included.
If using FROM/TO command, the unit of read/write of CR is one number for
one time. If using DFROM/DTO command, the unit of read/write of CR is two
numbers in one time.
CR #10
CR #9
Upper 16-bit Lower 16-bit
Specified CR number
The number of transmission groups n. The meaning of n=2 of 16-bit command
and n=1 of 32-bit are the same.
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
CR #5
CR #6
CR #7
CR #8
CR #9
CR #10
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
CR #5
CR #6
CR #7
CR #8
CR #9
CR #10
Specified device
Specified CR
Specified device Specified CR
16-bit command when n=6
32-bit command when n=3
In ES series models, flag M1083 is not provided. When FROM/TO command is
executed, all interrupts (including external or internal interrupt subroutines) will be
disabled. All interrupts will be executed after FROM/TO command is completed.
Besides, FROM/TO command also can be executed in the interrupt subroutine.
The function of the flag M1083 (FROM/TO mode exchange) provided in EP/EH
series models:
1. When M1083=Off, FROM/TO command is executed, all interrupts (including
external or internal interrupt subroutines) will be disabled. All interrupts will be
executed after FROM/TO command is completed. Besides, FROM/TO
command also can be executed in the interrupt subroutine.
2. When M1083=On, if an interrupt occurs while FROM/TO command has been
programmed, FROM/TO command will be interruptted to execute the interrupt.
However, FROM/TO command cannot be executed in the interrupt subroutine.




















