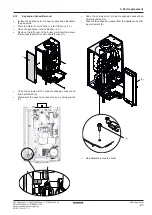
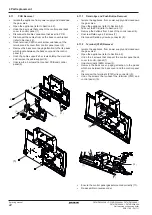
D2CND0 D2CND0 D2TND0
D2TND0 D2TND024A4AA
Wall-mounted condensing boiler
ESIE17-09 / 2017.11
Servicing manual
35
Explanations of parameters related with weather compen
-
sation are given in “Service parameters” and “User settings
menu” sections.
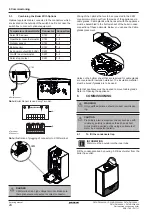
7.10.6.2 Effect of Heating Slope to CH Temperature
The effect of heating slope is illustrated on the graph below;
7.10.7 Scot Parameters (C) Safety combustion techno
-
logy system
The PCB of the appliance provides continuous control of com
-
bustion efficiency and combustion performance by means of
SCOT system. Due to SCOT system, gas valve operation is
independent of fan, so there is no need to gas valve adjust
-
ment for gas/air ratio optimization.
Ionization electrode senses a current from the flame which is
on the surface of the burner, and transmits the current to the
PCB at the level of µA.
PCB evaluates the transmitted current as a “point” value. This
value is defined as the “ion” in SCOT software.
By controlling ionization continuously, SCOT system ensures
the fuel / air mixture homogenously for each gas type.
Frequently occuring combustion and ignition
related errors can be resolved by optimizing the
parameters. C parameters are explained in detail
at following section.
INFORMATION
When the flue duct is not installed properly, SCOT
system breakdown errors occur often. Make sure
that flue duct is mounted properly on the boiler for
smooth operation.
WARNING
7.10.7.1 Detailed Explanations of C Parameters
C00:
This parameter is used to switch between fuel types. If
natural gas is to be used as supply gas, parameter must be
adjusted to “0” (zero). If LPG is to be used as supply gas, pa
-
rameter must be adjusted to “1” (one).
C01:
If a gas valve is at the limits of production tolerances,
starting gas/air ratio will be far from average value which may
also result in ignition problems (delayed or loud ignition). If
such problems are present, C02 parameter must be optimized
first. If C02 parameter change is not helping the ignition prob
-
lem, offset parameter can be the real reason. Increasing the
offset value will enrich the starting gas mixture which will help
delayed ignition problems.
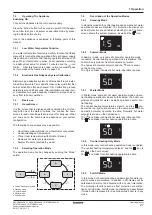
7 Operation
a
b
c
d
f
g
e
+
+
+
=
a Outdoor Temperature
b ODS correction P02
c Building estimation P01
d CH water temp. calculation
e Target CH water temperature
f Heating slope U01
g Virtual room temp. setpoint
(5)
(6)
(8)
(10)
(12)
(16)
(20)
(24)
(30)
10
20
0
-10
-20
-3030
40
50
60
70
80
Resultant boiler set point (ºC)
Room set point 22 (ºC)
Outside temperature (ºC)
min. (ºC)
Array of heating slopes max. (ºC)
Following parameters have impact to weather compensation
calculation:
•
•
Outdoor sensor correction (Parameter P02 )
•
Building estimation (Parameter P01)
•
Heating slope (Parameter U01)
•
Virtual room temperature set point
Calculation of CH temperature set point in principal is shown
below;
7.10.6.1 Weather compensation calculation
The required central heating temperature is calculated ac
-
cording to the outside temperature and the virtual room tem
-
perature set point, which is adjusted by left dial.
Note:
If the outside temperature falls, the central heating tem
-
perature will be increased.
SCOT PARAMETER SETTINGS
Parame-
ter No
Description
Unit
Fac-
tory
setting
Range
C00
Gas type
none 0
0 - 1
C01
Adjustment of gas
start offset
%
0
-9 - 20
C02
Adjustment of startup
capacity
%
0
-8 - 7
C03
Flue duct adjustment %
0
-5 - 10
C04
Adjustment minimum
capacity
%
0
0 - dyn.
max.
C05
Gas control offset
%
29.3
17 - 44
C06
Flame ionization
signal
pts
-
0 - 100
C07
Gas valve control
PWM
%
-
0 - 100
C08
Actual capacity value
%
-
0 - 100
C09
Ionization base value pts
-
0 - 255
C10
Minimum start ioniza
-
tion value
pts
-
0 - 255
C11
Ignition time
s
-
0 - 4.5
C12
Reducing ion base
value
pts
-
-5 - 10
C13
Reducing ion at mini
-
mum capacity
pts
-
-5 - 10
CE
Password entry
none -
0 - 999