Table 43: Group 40: Process PID Set 1
Code Description
Range
Resolution
Default
S
4001 GAIN
0 .1… 100 .0
0 .1
2 .5
Defines the PID Controller’s gain.
• The setting range is 0 .1… 100 .
• At 0 .1, the PID Controller output changes one-tenth as much as the error value .
• At 100, the PID Controller output changes one hundred times as much as the error value .
Use the proportional gain and integration time values to adjust the responsiveness of the system .
• A low value for proportional gain and a high value for integral time ensures stable operation, but provides sluggish response .
If the proportional gain value is too large or the integral time too short, the system can become unstable .
Procedure:
• Initially, set:
• 4001 GAIN = 0 .1 .
• 4002 INTEGRATION TIME = 20 seconds .
• Start the system and see if it reaches the set point quickly while maintaining stable operation . If not, increase GAIN (4001) until the actual signal
(or drive speed) oscillates constantly . It may be necessary to start and stop the drive to induce this oscillation .
• Reduce GAIN (4001) until the oscillation stops .
• Set GAIN (4001) to 0 .4 to 0 .6 times the above value .
• Decrease the INTEGRATION TIME (4002) until the feedback signal (or drive speed) oscillates constantly . It may be necessary to start and stop
the drive to induce this oscillation .
• Increase INTEGRATION TIME (4002) until the oscillation stops .
• Set INTEGRATION TIME (4002) to 1 .15 to 1 .5 times the above value .
• If the feedback signal contains high frequency noise, increase the value of Parameter 1303 FILTER AI1 or 1306 FILTER AI2 until the noise
is filtered from the signal.
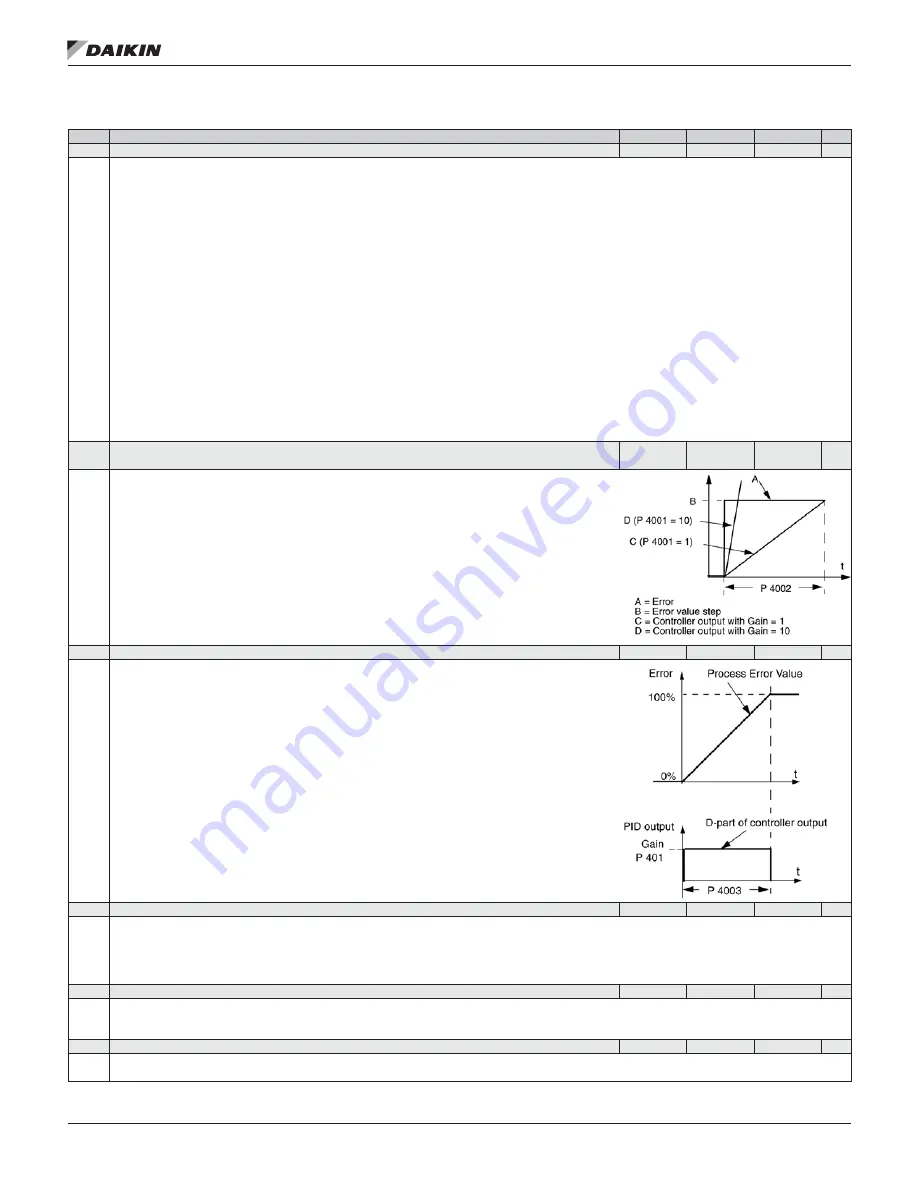
4002 INTEGRATION TIME
0 .0…
3600 .0 s
0 .1 s
3 .0 s
Defines the PID Controller’s integration time. Integration time is, by definition, is the time required
to increase the output by the error value:
• Error value is constant and 100% .
• Gain = 1 .
• Integration time of 1 second denotes that a 100% change is achieved in 1 second .
0 .0 = NOT SEL – Disables integration (I-part of controller) .
0 .1…3600 .0 = Integration time (seconds) .
See 4001 for adjustment procedure .
4003 DERIVATION TIME
0 .0… 10 .0 s
0 .1 s
0 .0 s
Defines the PID Controller’s derivation time.
• You can add the derivative of the error to the PID controller output . The derivative is the error value’s
rate of change . For example, if the process error value changes linearly, the derivative is a constant
added to the PID controller output .
• The error-derivative is filtered with a 1- pole filter. The time constant of the filter is defined by parameter
4004 PID DERIV FILTER .
0 .0 = NOT SEL – Disables the errorderivative part of the PID controller output
0 .1…10 .0 = Derivation time (seconds)
4004 PID DERIV FILTER
0 .0… 10 .0 s
0 .1 s
0 .1 s
Defines the filter time constant for the error-derivative part of the PID controller output.
• Before being added to the PID controller output, the error-derivative is filtered with a 1-pole filter.
• Increasing the filter time smooths the error-derivative, reducing noise.
0.0 = NOT SEL – Disables the error-derivative filter.
0 .1…10 .0 = Filter time constant (seconds) .
4005 ERROR VALUE INV
0, 1
—
0
Selects either a normal or inverted relationship between the feedback signal and the drive speed .
0 = NO – Normal, a decrease in feedback signal increases drive speed . Error = Ref - Fbk
1 = YES – Inverted, a decrease in feedback signal decreases drive speed . Error = Fbk - Ref
4006 UNITS
0…31
—
4
Selects the unit for the PID controller actual values . (PID1 parameters 0128, 0130, and 0132) .
• See parameter 3405 for list of available units .
a
CTual
s
Ignals
and
p
arameTers
www .DaikinApplied .com 63
OM 1190-1 • MD4 VFD
Содержание ACS320
Страница 115: ......
















































