DVG-5004S User’s Manual
VoIP Gateway Configuration
D-Link Systems, Inc.
60
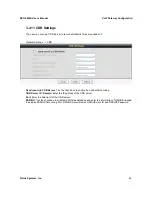
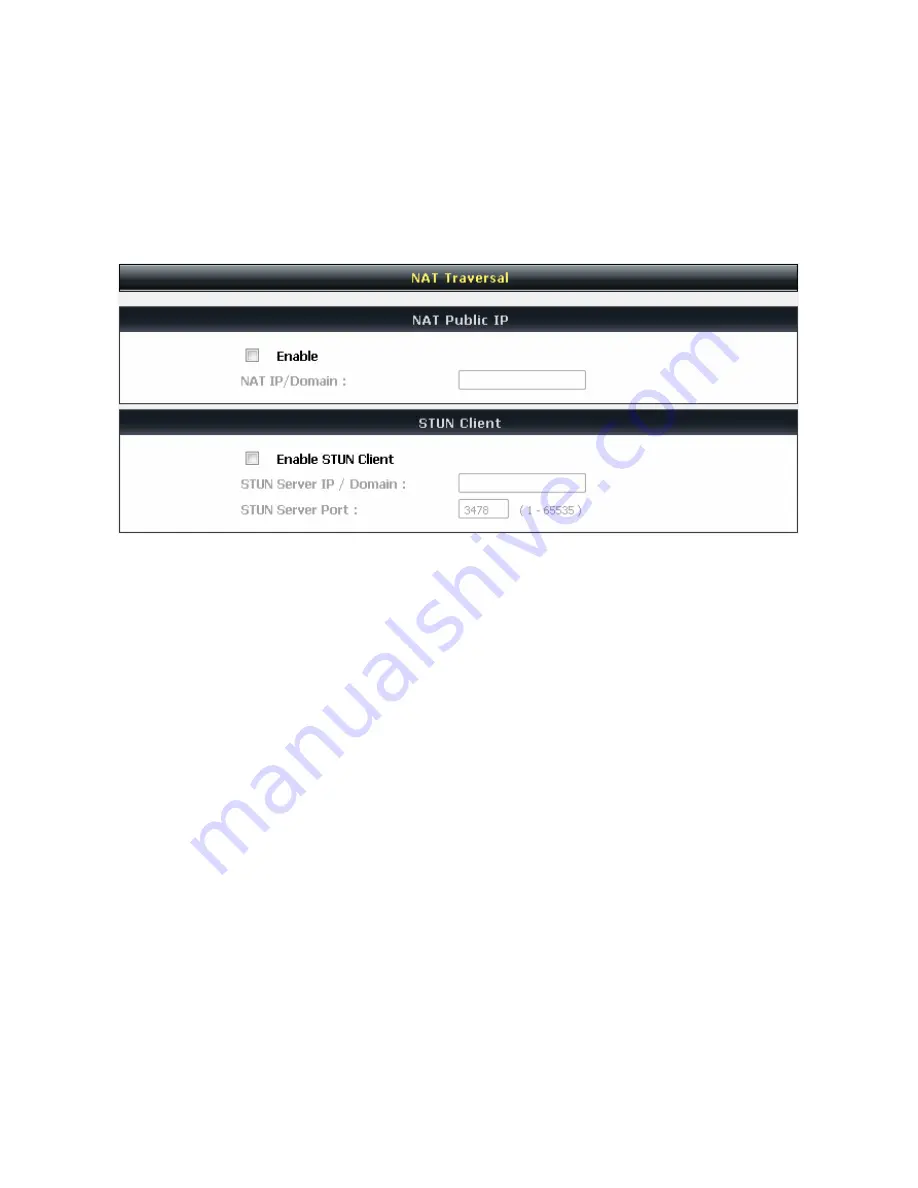
3-4-10 NAT Traversal
If your VoIP Gateway is set up behind an Internet sharing device, you can select either the NAT or STUN
protocol.
Advanced Settings
→
NAT Traversal
Enable(NAT Public IP):
Check the box to use the IP address of the Internet sharing device if the VoIP
Gateway is set up behind an Internet sharing device. Also the VoIP Gateway will use the IP address of the
Internet sharing device as the public IP when it connects to Internet. Furthermore, some of the Internet
sharing device’s type is symmetric NAT. You need to set Virtual Server or Port Mapping (Forwarding) from
the Internet sharing device for the listen port and communication ports (RTP ports) of the VoIP Gateway.
NAT IP/Domain:
Enter the real public IP address of the IP sharing device or the router; or enter a true URL
(Uniform Resource Locator) when DDNS is used. Please refer to the DDNS settings.
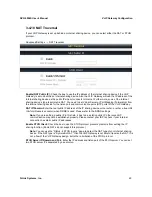
Note:
If you are setting a public IP in this field, it has to be a static public IP, otherwise VoIP
communication may not be established properly. Please contact your ISP to check if your Internet
connection has static public IP addresses.
Enable STUN Client:
Check the box to use the STUN protocol prevents problems from setting the IP
sharing function. (Some NATs do not support this protocol.)
Note:
You can use the “Status
Æ
STUN Inquiry” page to detect the NAT type of your Internet sharing
device. If the NAT type is “Symmetric NAT,” then the VoIP Gateway is not able to traverse the NAT. It is
not a flaw of the VoIP Gateway design, but rather a limitation of the STUN protocol.
STUN Server IP/Domain and Port:
Enter the IP address and listen port of the STUN server. You can set
two STUN server IPs separated by a semicolon.