Chapter 1 Product Overview
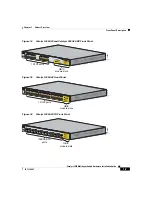
Front-Panel Description
1-8
Catalyst 3550 Multilayer Switch Hardware Installation Guide
78-11358-03
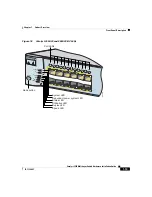
10/100 and 10/100/1000 Ports
You can set the 10/100 and 10/100/1000 ports on the switch to operate in any
combination of half duplex, full duplex, 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or 1000 Mbps
(1000 Mbps if so equipped). You can also set these ports for speed and duplex
autonegotiation in compliance with IEEE 802.3AB. (The default setting is
autonegotiate.) When set for autonegotiation, the port senses the speed and duplex
settings of the attached device and advertises its own capabilities. If the connected
device also supports autonegotiation, the switch port negotiates the best
connection (that is, the fastest line speed that both devices support and full-duplex
transmission if the attached device supports it) and configures itself accordingly.
In all cases, the attached device must be within 100 meters.
Note
100BASE-TX and 1000BASE-T traffic requires Category 5 cable. 10BASE-T
traffic can use Category 3 or Category 4 cables.
When connecting the switch to workstations, servers, routers, and Cisco IP
Phones, be sure that the cable is a straight-through cable. When connecting the
switch to switches or hubs, use a crossover cable. When using a straight-through
or crossover cable for 1000BASE-T connections, be sure to use a twisted
four-pair, Category 5 cable for proper operation. Pinouts for the cables are
described in
Appendix B, “Connector and Cable Specifications.”
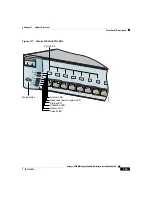
100BASE-FX Ports
The 100BASE-FX ports use 50/125- or 62.5/125-micron multimode fiber-optic
cabling. In full-duplex mode, these ports only operate at 100 Mbps.
In full-duplex mode (the default), the cable length from a switch to an attached
device cannot exceed 6562 feet (2 kilometers).
You can connect a 100BASE-FX port to an SC or ST port on a target device by
using one of the MT-RJ fiber-optic patch cables listed in
. Use the Cisco
part numbers in
to order the patch cables that you need.