Chapter 4: System Configuration
724-746-5500 | blackbox.com
25
4.5.2 PuTTY
You can also use communications packages like
PuTTY
to connect to the
console server
command line (and to connect serially attached devices as
covered in
Chapter 5
).
PuTTY
is a freeware implementation of Telnet and SSH for Windows and UNIX platforms. It runs as an executable application
without needing to be installed onto your system.
PuTTY
(the Telnet and SSH client itself) can be downloaded from
http://www.tucows.com/preview/195286.html
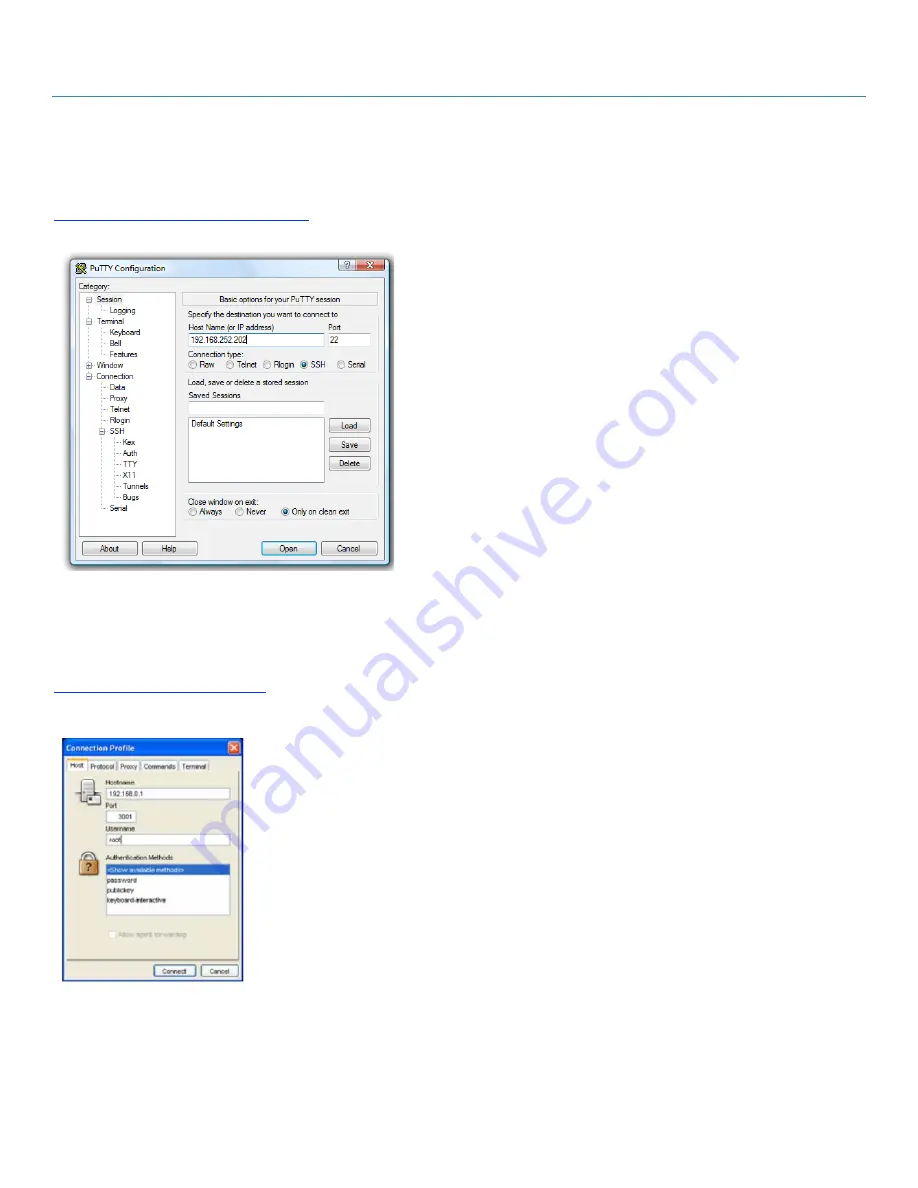
To use PuTTY for an SSH terminal session from a Windows
client, enter the
console server
’s IP address as the ”Host
Name (or IP address).”
To access the
console server
command line, select “SSH” as
the protocol, and use the default IP Port 22.
Click “Open” and the
console server
login prompt will
appear. (You may also receive a “Security Alert” that the
host’s key is not cached. Choose “yes” to continue.)
Using the Telnet protocol is similarly simple, but you use the
default port 23.
Figure 4-8. PuTTY screen.
4.5.3 SSHTerm
Another popular communications package you can use is
SSHTerm,
an open source package that you can download from
http://sourceforge.net/projects/sshtools
To use
SSHTerm
for an SSH terminal session from a Windows Client, simply Select the “File” option and click on “New Connection.”
A new dialog box will appear for your “Connection Profile.” Type in the host
name or IP address (for the
console server
unit) and the TCP port that the SSH
session will use (port 22). Then type in your username, choose password
authentication, and click connect.
You may receive a message about the host key fingerprint. Select “yes” or
“always” to continue.
The next step is password authentication. The system prompts you for your
username and password from the remote system. This logs you on to the
console server
Figure 4-9. Connection Profile screen.















































