BP-LFP-2725(D)
Revision 1-2
12
E Functionality of BMS
If the BMS is in ACTIVE MODE, diverse critical parameters of the battery system (such as voltages, currents, etc.)
are monitored cyclically by battery management system for compliance with the limits. In the event of a fault,
the battery system disconnects the main current path. Charging and discharging is only possible with an acti-
vated battery management system
E1 Protection functions
The BMS has several possibilities for detecting fault conditions. The following is a basic breakdown into short-
term, reversible and permanent errors:
If a short-term, reversible fault occurs during operation (e.g. overcurrent, overtemperature), the electronics will
switch off briefly and then switch on again when the fault no longer exists, otherwise the battery will remain
deactivated.
If a permanent fault occurs during operation (e.g. loss of a cell voltage tap, deep discharge), the battery remains
permanently deactivated and can only be re-enabled by the manufacturer (after troubleshooting).
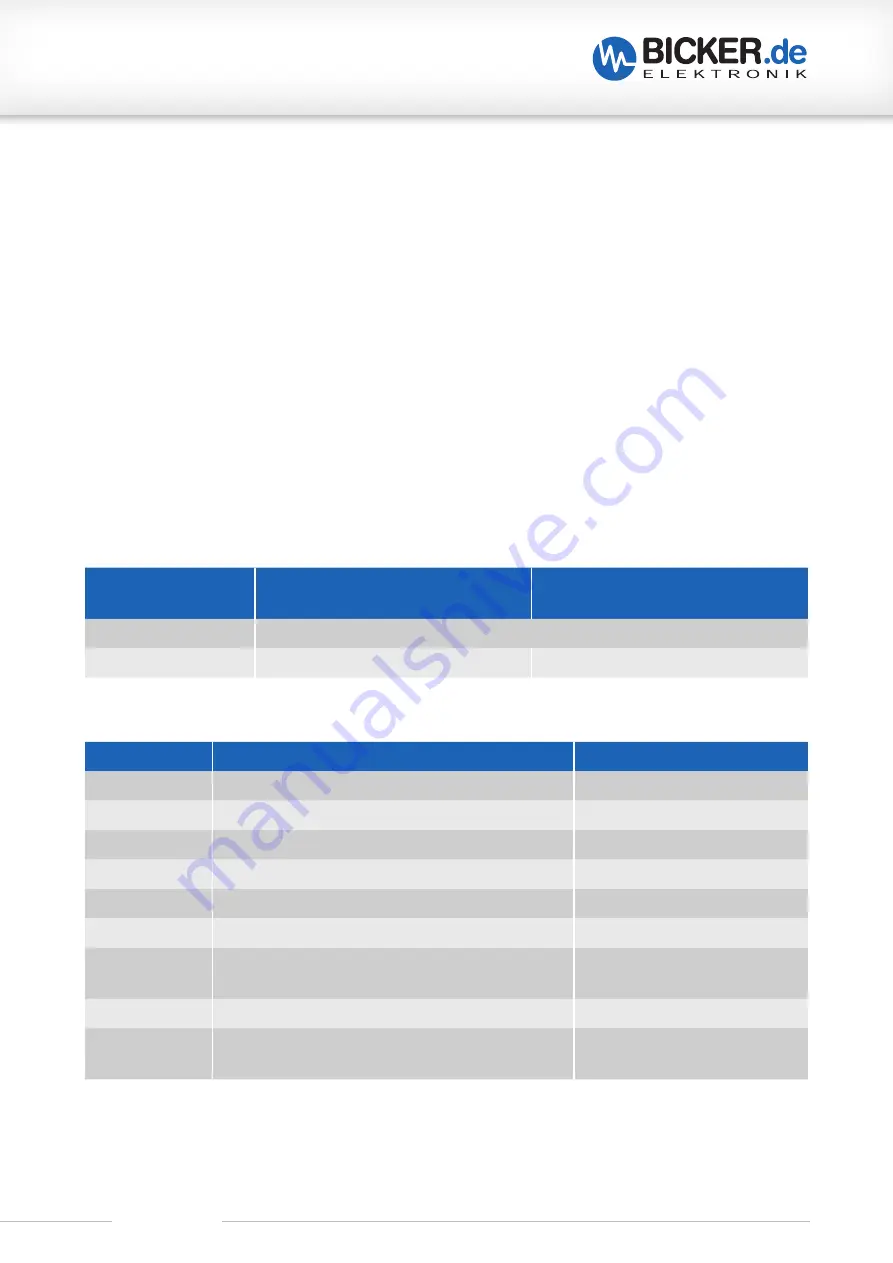
Limits for short-term, reversible errors:
Short circuit and overload detection
Over- and undervoltage detection
(cell)
First level of security
Switch off by balancing IC
Second level of security 15 A fuse
Thermic fuse
Abbreviation
Description
Limit values
CUV
Cell undervoltage detection
2.4 V (Recovery 3.1 V)
COV
Cell overvoltage detection
3.65 V (Recovery 3.3 V)
OCD
Overcurrent detection during discharging
18 A (50 ms)
ASCD
Short-circuit detection during discharging
~64 A (200 µs)
OCC
Overcurrent detection during charging
6 A (160 ms)
OTC
Overtemperature detection of cells during charging
+65 °C (Re60 °C)
OTD
Overtemperature detection of cells during
discharging
+75 °C (Re70 °C)
UTC
Undertemperature detection of cells during charging –30 °C (Recovery –25 °C)
UTD
Undertemperature detection of cells during
discharging
–30 °C (Recovery –25 °C)