12
ULTRA-Q PRO PEQ2200
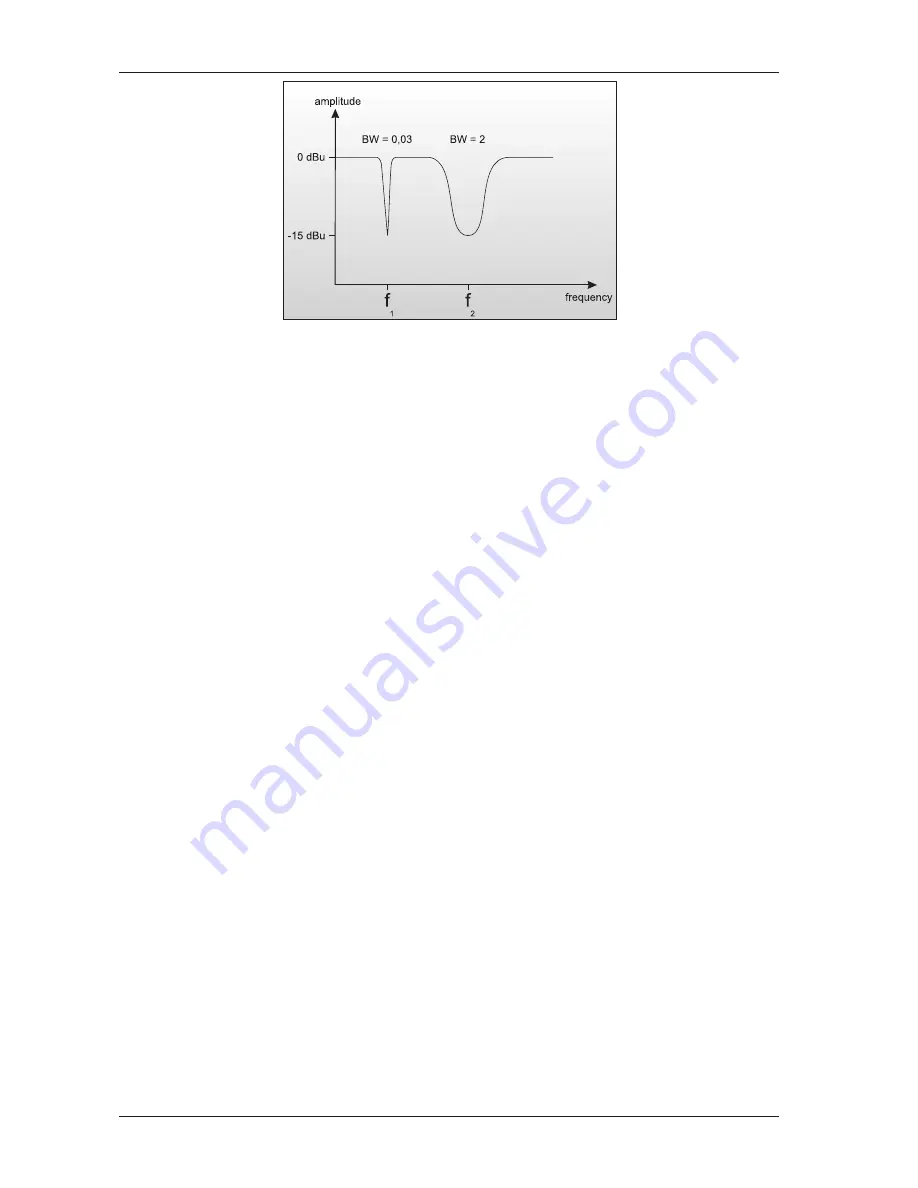
Fig. 5.1: Various filter qualities
During operation you can switch on and off the individual bands to make an A/B comparison between the
equalizer effect and the unprocessed signal. Due to the complex and partly difficult settings of parametric
equalizers such a facility is indispensable. Still, most parametric EQs have no band-specific in/out switches
which makes it difficult to keep track of what the various switches and controls do.
5.2 The Constant-Q principle
One of the most important features any graphic or parametric equalizer has to offer is the independent control
of its various parameters. The special state-variable filters of the ULTRA-Q PROs use the so-called Constant Q
principle which prevents the parameters frequency, bandwidth and amplitude from influencing each other.
In the same way, the mutual influence of the individual frequency bands is avoided, which is a fundamental
requirement as it allows for clearly defined and repeatable filter settings. When several filters are used
simultaneously, the resulting overall filter curve can be calculated by adding/subtracting the single
band-specific filter curves.
5.3 The concept of parallel filters
Unlike conventional parametric equalizers the ULTRA-Q PRO features a parallel filter configuration, which
offers a decisive advantage over series-type configurations: with parallel filters it is possible to reduce to a
minimum the phase shifts and delays usually associated with filters, which is the reason why the ULTRA-Q
PRO is such a musical device.
Naturally, this concept, too, is subject to a few limitations: unlike series-type filter configurations the concept
of parallel filters allows only to a limited extent for an extreme boost/cut of frequencies. However, as extreme
settings are usually the result of an improperly adjusted sound image, it is imperative that deficiencies of this
kind be identified and eliminated, before the actual musical fine-tuning of the sound image takes place. Still,
extreme settings can be realized by overlapping the frequencies of the individual bands.
5.4 Filter functions
5.4.1 The notch function
With notching or peaking we describe the specific attenuation of single frequencies or frequency bands. A
notch filter produces an effect that is the opposite to a band-pass filter.
5. TECHNICAL BACKGROUND







































