Building Automation Products, Inc., 750 North Royal Avenue, Gays Mills, WI 54631 USA
Tel:+1-608-735-4800 • Fax+1-608-735-4804 • E-mail:[email protected] • Web:www.bapihvac.com
Specifications subject to change without notice.
4 of 4
Installation & Operating Instructions
rev. 08/21/17
28173_ins_CO2_Duct
CO
2
Duct and Rough Service Sensor
Diagnostics
Possible Problems:
Possible Solutions:
General troubleshooting
Determine that the input is set up correctly in the controller's and building automation
software.
Check wiring at the sensor and controller for proper connections.
Check for corrosion at either the controller or the sensor. Clean off the corrosion,
re-strip the interconnecting wire and reapply the connection. In extreme cases,
replace the controller, interconnecting wire and/or sensor.
Check the wiring between the sensor and controller. Label the terminals at the
sensor end and the controller end. Disconnect the interconnecting wires from the
controller and the sensor. With the wires disconnected, measure the resistance from
wire-to-wire with a multimeter. The meter should read greater than 10 Meg-ohms,
open or OL depending on the meter. Short the interconnecting wires together at
one end. Go to the other end and measure the resistance from wire-to-wire with a
multimeter. The meter should read less than 10 ohms (22 gauge or larger, 250 feet
or less). If either test fails, replace the wire.
Check power supply/controller voltage supply
Disconnect sensor and check power wires for proper voltage (see specifications on
page 4)
Incorrect CO
2
Wait 15 minutes after a power interruption.
Check all BAS controller software parameters.
Determine if the sensor is exposed to an external environment different from the duct
area that is being measured.
If the sensor is reading consistently high, make sure that the power supply to the unit
can provide 240mA. A low power situation will cause high CO
2
readings.
Note: If the CO
2
sensor has consistently given high PPM readings for over 5 days, it
will take up to 14 days for the readings to return to normal.
For the sensor to work correctly, the wiring entrance must remain air tight. If
the CO
2
transmitter is mounted to a hollow wall and wired through its back, or
wired with conduit, it is possible that a draft of clean air may fill the enclosure
through the wiring opening. This draft may prevent the unit from measuring
ambient CO
2
. BAPI recommends either a liquid-tight fitting or plugging the
conduit at the enclosure.
• Liquid-Tight Fitting
– BAPI’s Liquid-Tight Fitting (BA/LTF) allows wire
cables of 0.1 to 0.3 inch outside diameter to enter the box. Tightening the
collar onto the wire cable keeps the wiring entrance air tight.
• Conduit
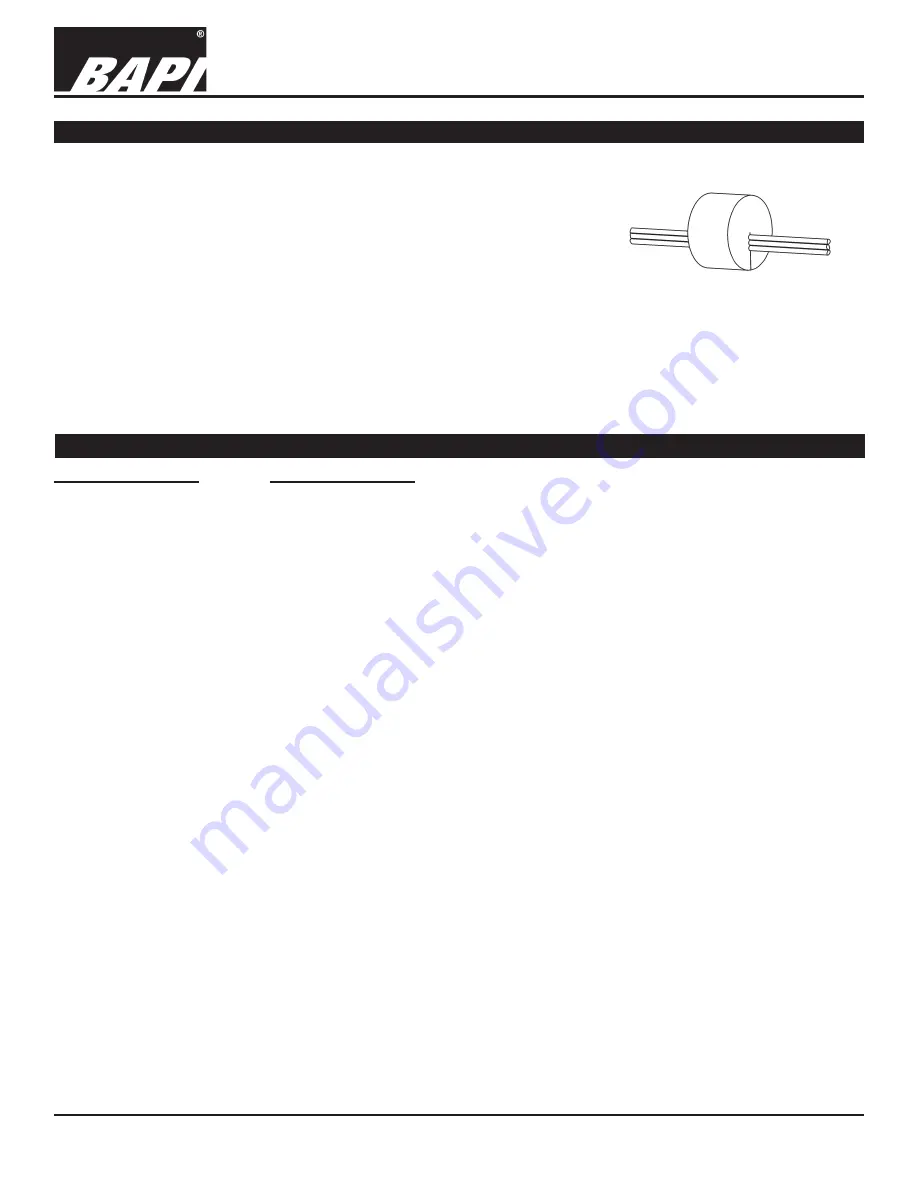
– Included with the CO
2
transmitter is a foam plug to seal the ½
inch EMT. Place the wires into the plug as shown in Fig. 10 and then insert
the plug into the conduit sealing the conduit.
Fig. 10:
Wires Through Foam Plug
Keeping the Enclosure Air Tight After Termination






















