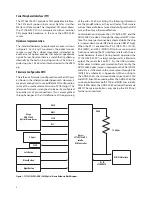
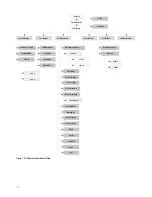
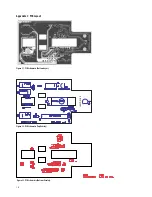
9
ReadDeltaY
– Reads the ADNS-3080 Delta_Y register for the
Y movement. Calls the
ReadSPI
routine to enable the SPI
interface and perform reading operations through the
four-wire serial interface. Any new Y motion information
is added to the
[yCount]
variable.
WriteSPI
– Writes to the ADNS-3080 register. A write op-
eration consists of two bytes. The fi rst byte contains the
address (7 bits) and has “1” as its MSB. The second byte
contains data. The microcontroller to drive both the SCLK
and the MOSI lines.
SPIWriteRoutine
is called to carry the
write operation.
ReadSPI
– Reads the desired ADNS-3080 registers. A read
operation is composed of two parts. First, the microcon-
troller performs a write to the ADNS-3080, sending the
address of the target register to be read. The microcon-
troller drives both the SCLK and MOSI lines. After t
SRAD
delay, the ADNS-3080 will drive the data via MISO. The
microcontroller is only driving the SCLK line (outputs
SCLK for the serial interface).
SPIWriteRoutine
is called to
carry the write operation.
SPIWriteRoutine
– Writes the data to be transmitted onto
the SPI pins.
CheckProductID
– This function checks the product ID of the
sensor chip being used. The ID returned should match
with the ADNS-3080’s ID.
GetButtons
– Returns the current state of the buttons.
USB Functions
usbMain
– This routine initializes the USB related pa-
rameters and enables VREG to signal the host that the
mouse has been connected. The program then goes to
the
usbTaskLoop
.
usbTaskLoop
– This function spins in an infi nite loop waiting
for an event that needs servicing. The
ProcessButtons
and
ReadProcessOptics
functions are called within this loop to
retrieve any new motion or button information. The data
received from these functions will be loaded into the
endpoint 1 buff er to be sent to the host.
ep0SetupReceived
– This routine is entered whenever a
SETUP packet is received on endpoint 0. It parses the
packet and calls the appropriate routine to handle the
packet.
ep0InReceived
– This routine is entered whenever an IN
packet is received on endpoint 0.
ep0OutReceived
– This routine is entered whenever an OUT
packet is received on endpoint 0.
setDeviceConfi guration
– This routine is entered when a SET
CONFIGURATION request has been received from the
host.
setDeviceAddress
– This routine is entered whenever a SET
ADDRESS request has been received. The device address
change cannot take place until after the status stage of
this no-data control transaction. So the address is saved
and a fl ag is set to indicate that a new address was just
received. The code that handles IN transactions will rec-
ognize this and set the address properly.
getDescriptor
– This routine is entered when a GET DESCRIP-
TOR request is received from the host. This function
decodes the descriptor request and sends the proper
descriptor.
setInterfaceIdle
– This routine is entered whenever a SET
IDLE request is received. See the HID specifi cation for
the rules on setting idle periods. This function sets the
HID idle time. See the HID documentation for details on
handling the idle timer.
setInterfaceProtocol
– This routine is entered whenever a
SET PROTOCOL request is received. This no-data control
transaction enables boot or report protocol.
getInterfaceReport
– This routine is entered whenever a GET
REPORT request is received.
getInterfaceIdle
– This routine is entered whenever a GET
IDLE request is received. This function then initiates a
control-read transaction that returns the idle time. See
the HID class documentation for more details.
getInterfaceProtocol
– This routine is entered whenever a GET
PROTOCOL request is received. This request initiates a
control-read transaction that tells the host if the mouse is
confi gured for boot or report protocol. See the HID class
documentation for more details.
getDeviceConfi guration
– This routine is entered whenever
a GET CONFIGURATION Request is received. This func-
tion then starts a control read transaction that sends the
confi guration, interface, endpoint, and HID descriptors
to the host.
requestNotSupported
– Unsupported or invalid descriptor
requests will cause this fi rmware to STALL these transac-
tions.