17
STF-R/C/D/IP Hardware Manual
920-0141 Rev. A
6/5/2018
Your PC, or any other device that you use to communicate with the drive, will also have a unique address.
On the drive, switch settings 1 through E use the standard class B subnet mask (i.e. “255.255.0.0”). The mask for the universal
recovery address is the standard class A (i.e. “255.0.0.0”).
One of the great features of Ethernet is the ability for many applications to share the network at the same time. Ports are used to direct
traffic to the right application once it gets to the right IP address. The UDP eSCL port in our drives is 7775. To send and receive
commands using TCP, use port number 7776. You’ll need to know this when you begin to write your own application. You will also
need to choose an open (unused) port number for your application. Our drive doesn’t care what that is; when the first command is sent
to the drive, the drive will make note of the IP address and port number from which it originated and direct any responses there. The
drive will also refuse any traffic from other IP addresses that is headed for the eSCL port. The first application to talk to a drive “owns”
the drive. This lock is only reset when the drive powers down.
If you need help choosing a port number for your application, you can find a list of commonly used port numbers at http://www.iana.
org/assignments/port-numbers.
One final note: Ethernet communication can use one or both of two “transport protocols”: UDP and TCP. eSCL commands can be
sent and received using either protocol. UDP is simpler and more efficient than TCP, but TCP is more reliable on large or very busy
networks where UDP packets might occasionally be dropped.
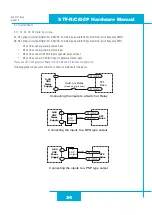
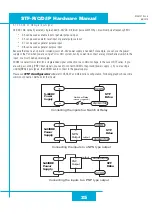
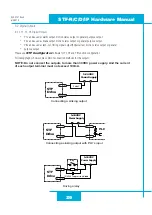
Option 1: Connect a Drive to Your Local Area Network
If you have a spare port on a switch or router and if you are able to set your drive to an IP address that is compatible with your network,
and not used by anything else, this is a simple way to get connected. This technique also allows you to connect multiple drives to your
PC. If you are on a corporate network, please check with your system administrator before connecting anything new to the network. He
or she should be able assign you a suitable address and help you get going.
If you are not sure which addresses are already used on your network, you can find out using “Angry IP scanner”, which can be
downloaded free from http://www.angryip.org/w/Download. But be careful: an address might appear to be unused because a computer
or other device is currently turned off. And many networks use dynamic addressing where a DHCP server assigns addresses “on
demand”. The address you choose for your drive might get assigned to something else by the DHCP server at another time.
Once you’ve chosen an appropriate IP address for your drive, set the rotary switch according the address table above. If none of the
default addresses are acceptable for your network, you can enter a new table of IP addresses using Configurator. If your network uses
addresses starting with 192.168.0, the most common subnet, you will want to choose an address from switch settings 4 through E.
Another common subnet is 192.168.1. If your network uses addresses in this range, the compatible default selections are 1, 2 and 3.
If your PC address is not in one of the above private subnets, you will have to change your subnet mask to 255.255.0.0 in order to talk
to your drive. To change your subnet mask:
• 1. On Windows XP, right click on “My Network Places” and select properties. On Windows 7, click Computer. Scroll down the left
pane until you see “Network”. Right click and select properties. Select “Change adapter settings”
• 2. You should see an icon for your network interface card (NIC). Right click and select properties.
• 3. Scroll down until you see “Internet Properties (TCP/IP)”. Select this item and click the Properties button. On Windows 7 and
Vista, look for “(TCP/IPv4)”
• 4. If the option “Obtain an IP address automatically” is selected, your PC is getting an IP address and a subnet mask from the
DHCP server. Please cancel this dialog and proceed to the next section of this manual: “Using DHCP”.
• 5. If the option “Use the following IP address” is selected, life is good. Change the subnet mask to “255.255.0.0” and click OK.