18
the output operating in the retransmission mode enables the conversion of the input signal to the output signal
(in the range
ArLo
÷
ArHi
). In the control output mode, the control parameters and functions are the same as for
the related output 1/2/3, but the variability range of the analog signal is continuous (0 ÷ 100%) only for the PID
algorithm (
chapter 9.3
) and manual operation, for the control of ON-OFF type with hysteresis, the output has
extreme values (bottom or upper value, e.g. 0mA = 0% = OFF or 20mA = 100% = ON) without intermediate values,
which can be used e.g. to activate the SSR relay.
The values of the output signal (mA/V) can be presented in the form of a bargraph on the bottom line of the
display (parameter 73:
dibo
=
bArA
) or read from the level of MODBUS-RTU/TCP and MQTT protocols,
chapter 11
.
Moreover,
it is
possible to
correct
(calibrate) the
range of
changes of the
output signal
(parameters 34:
cbot
and
35:
ctoP
).
9.3. PID CONTROL
The PID algorithm makes it possible to obtain smaller temperature
control errors than the ON-OFF method with hysteresis. However,
this algorithm requires selection of parameters characteristic for a
specific regulation object (eg a furnace). In order to simplify the
handling, the controller is equipped with advanced functions of PID
parameter selection, described in
chapter 9.4
. In addition, it is always
possible to manually adjust the settings (
chapter 9.5
).
The PID control for a given control output is active when one of the
three sets of PID parameters is selected (with the parameter
ctY1
/
2
/
3
, description in chapter 8, Table 8, point II
, or with the
parameter
PSE1
/
2
/
3
,
point V
), i.e.
PiD1
/
2
/
3
.
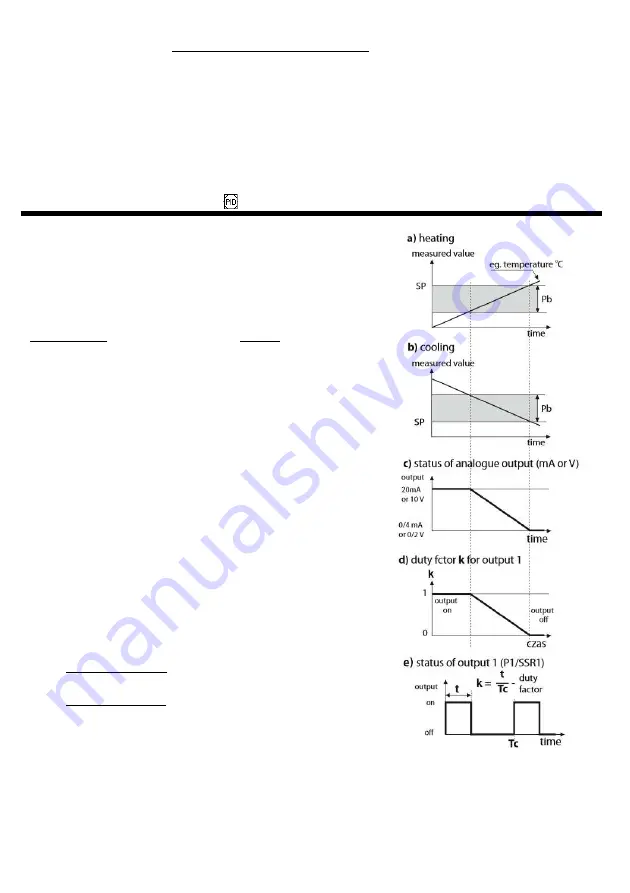
The position of the proportional band
Pb
(
Pb1
/
2
/
3
,
Table 8, point IV
)
in relation to the setpoint
SP
(
SEt1
/
2
/
3
) is shown in Figures 9.3 a)
and b). The parameters
ti1
/
2
/
3
and
td1
/
2
/
3
are responsible for the
influence of the integral and derivative element of the PID control.
The parameter
PEr1
/
2
/
3
sets the pulse period
Tc
for the P/SSR
output (it is also the time of its status update), while
oPF1
/
2
/
3
the
available power used for selecting PID parameters. If the PID
algorithm is implemented by the 0/4 ÷ 20mA or 0/2 ÷ 10V analog
output, the
Tc
period is irrelevant. The mA/V output signal is then
updated every 1 s and it can adopt intermediate values from the
entire range of output variability (0÷100%).
The principle of operation of the P-type control (proportional
control) for the P/SSR output is shown in figures d), e) for the analog
output, figure c).
Fig. 9.3.
Principle of PID regulation operation:
a)
position of the
Pb
proportional band in relation to the setpoint
SP
for the heating type control (
Fvn1
/
2
/
3
=
indH
)
b)
position of the proportional band
Pb
in relation to the setpoint
SP
for the cooling type control (
Fvn1
/
2
/
3
=
dirC
)
c)
the status of the analog output 0/4÷20 mA or 0/2÷10V
d)
duty factor
k
for a bi-state P/SSR output
e)
the status of the output for the measured value
PV
within the
Pb
range
























