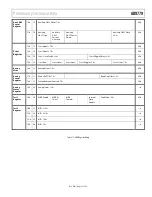
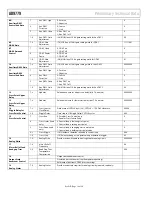
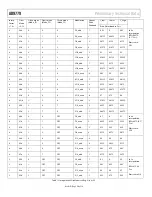
AD9779
Preliminary Technical Data
Rev. PrD | Page 22 of 34
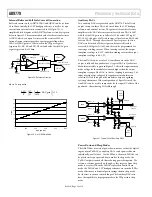
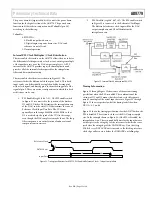
Internal Reference/Full Scale Current Generation
Full scale current on the AD9779 IDAC and QDAC can be set from
10 to 30ma. Initially, the 1.2V bandgap reference is used to set up a
current in an external resistor connected to I120 (pin 75). A
simplified block diagram of the AD9779 reference circuitry is given
below in
Figure 29
. The recommended value for the external resistor
is 10K
Ω
, which sets up an I
REFERENCE
in the resistor of 120
µ
a.
Internal current mirrors provide a current gain scaling, where
IDAC or QDAC gain is a 10 bit word in the SPI port register
(registers 0A, 0B, 0E, and 0F). The default value for the DAC gain
registers gives an I
FS
of 20ma.
1.2V bandgap
10K
Ω
0.1
µ
F
current scaling
DAC full scale
reference current
IDAC
QDAC
AD9779
IDAC gain
QDAC gain
I120
VREF
Figure 29 . Reference Circuitry
where I
FS
is equal to;
32
gain
DAC
1024
6
12
27
R
1.2V
×
⎟⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜⎜
⎝
⎛
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
×
+
×
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
0
200
400
600
800
1000
DAC gain code
I
FS
(m
a
)
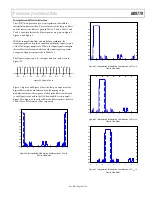
Figure 30. I
FS
vs. DAC Gain Code
Auxiliary DACs
Two auxiliary DACs are provided on the AD9779. The full scale
output current on these DACs is derived from the 1.2V bandgap
reference and external resistor. The gain scale from the reference
amplifier to the DAC reference current for each aux DAC is 16.67.
with the Aux DAC gain set to full scale (10 bit values, SPI reg 0C,
0D, 10, 11), this gives a full scale current of 2ma for Aux DAC1 and
for Aux DAC2. Through these same SPI port registers, the Aux
DACs can be turned off, their signs can be inverted (scale is
reversed, 0-1024 gives I
FS
to 0), and they can be programmed for
sourcing or sinking current. When sourcing current, the output
compliance voltage is 0-1.5V, and when sinking current the output
compliance voltage is 0.8-1.5V.
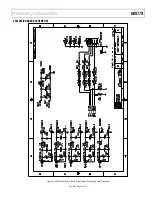
The Aux DACs can be used for LO cancellation when the DAC
output is followed by a quadrature. A typical DAC to Quadrature
Modulator interface is given in Figure 31. Often, the input common
mode voltage for the modulator is much higher than the output
compliance range of the DAC, so that ac coupling is necessary. The
input referred offset voltage of thee quadrature modulator can
result in LO feed through on the modulator output, degrading
system, performance. If the configuration of
Figure 29
is used, the
Aux DACs can be used to compensate for the input DC offset of the
quad mod, thus reducing LO feedthrough.
IOUT1_P
IDAC
QDAC
IOUT2_N
IOUT2_P
IOUT1_N
AUX1_P
AUX
DAC1
AUX2_N
AUX2_P
AUX1_N
AUX
DAC2
Quad Mod
I Inputs
Quad Mod
Q Inputs
Figure 31. Typical Use of Auxiliary DACs
Power Down and Sleep Modes
The AD9779 has a variety of power down modes, so that the digital
engine, main TxDACs, or auxiliary DACs can be powered down
individually, or all at once. Via the SPI port, the main TxDACs can
be placed in sleep or powered down modes. In sleep mode, the
TxDAC output is turned off, thus reducing power dissipation. The
reference remains powered on though, so that recovery from sleep
mode is very fast. When the TxDAC is placed in Power Down
mode, the TxDAC and 1.2V bandgap reference are turned off. This
mode offers more substantial power savings than in sleep mode,
but the time to turn on is much longer. The Auxiliary DACs also
have the capability to be programmed via the SPI port into sleep
mode.