Temposonics
®
MH Digital
Operating Manual
I
15
I
9. Communication objects
CANopen & CANopen Safety
The information flow of function data and user-specific information is subject to a data protocol according to OSI model (ISO 7498). The CiA
(CAN in Automation) user organization is in charge of the CAN bus technology and its further development.
During the „operational“ mode of operation, the evaluation electronics integrated in the sensor convert the measured information into CAN mes-
sages and send them onto the bus, where the information is read and processed by the control system. For this purpose, the characteristics and
functions of the sensor are stored in the internal object directory (see below).
The CAN bus uses the following communication objects for data transfer on the bus:
SDO (Service Data Object)
parameters relating to the sensor configuration are introduced or
read using the SDO. This is performed by access to the internal object
directory of the sensor. To process SDOs, the sensor must be in the
„pre-operational“ or „operational“ mode.
NMT (Network Management)
for control of the network and individual component status. Can be also used for monitoring using the following objects:
SYNC-Object
synchronizes the bus communication, i.e. synchronous PDOs are sent
to the control system after receiving a SYNC object.
Emergency-Object
sends error messages. As the priority of error messages is generally
higher than the priority of PDOs, error messages are transmitted prior
to PDOs.
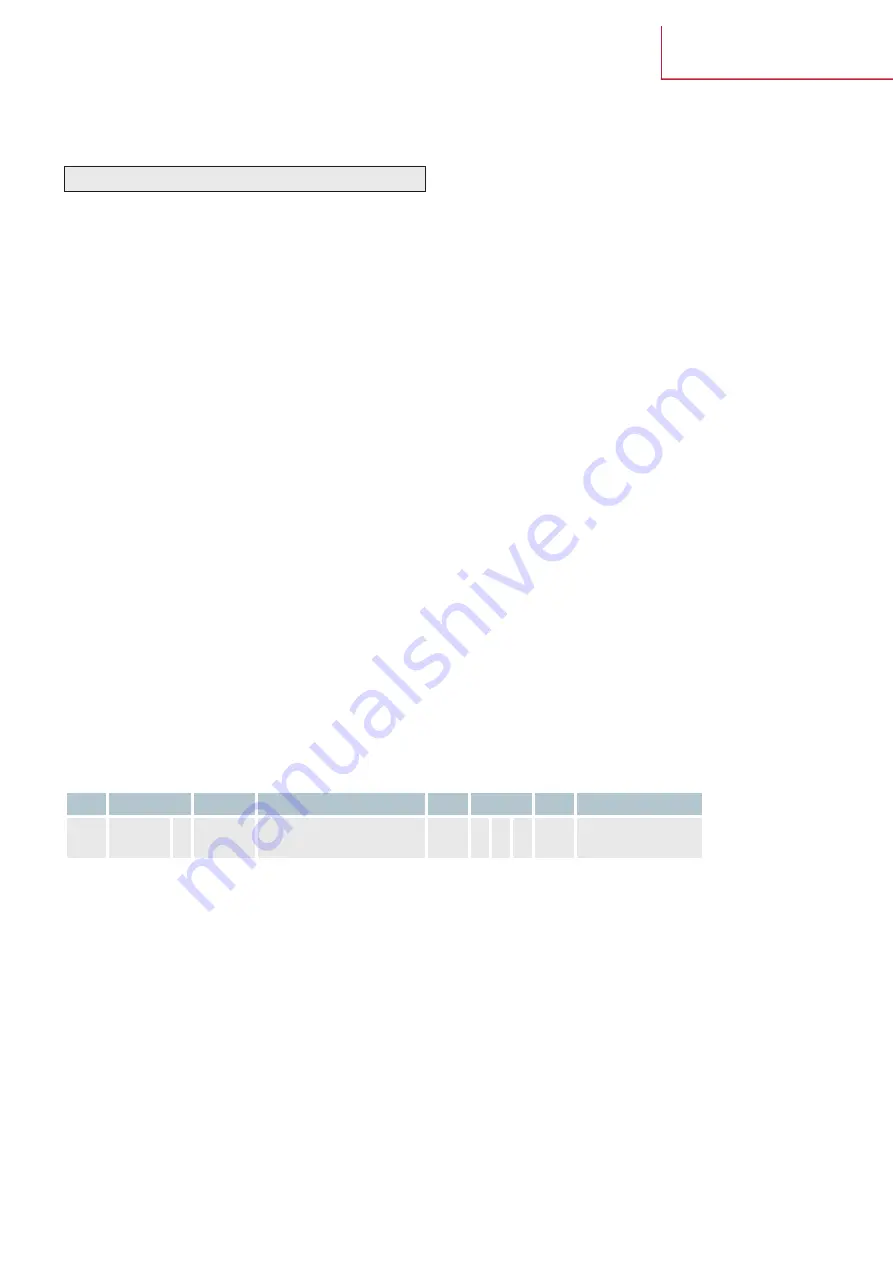
The structure of a message in the CANopen protocol is as follows:
SOF
Arbitration
Control
Data field
CRC
ACK
EOF
Interframe space
1
11
1
6
0..8
Bytes
15
1 1 1
7
≥ 3
Fig. CAN bus data protocol
CANopen Safety – Redundant Data Transmission
To meet the high safety requirements for SIL applications, the CANopen Safety protocol provides redundant data transmission of safety-critical
information. The safety functions are realized via special communication objects termed SRDOs (Safety Related Data Objects).
SRDO (Safety Related Data Objects)
For detection of transmission errors, messages are transferred redundantly in SRDOs. Each data set is sent in two separate messages, whereby
the second message is sent bitwisely inverted with a different identifier. The interval at which two SRDOs are sent is predetermined by the SRVT
(Safety Related Validation Time) and the SCT (Safeguard Cycle Time). This interval between two SRDOs must not be exceeded, otherwise the
SRDO is not valid and rejected by the receiver.
Heartbeat-Object
The Heartbeat Object is for error control purposes and signal the
presence of a node and its state. The Heartbeat is a periodic mes-
sage of a device to one or several other network nodes. It indi-
cates that the sending node is still working properly.
PDO (Process Data Object)
The real-time data transfer of position and velocity states is
performed by PDO messages and generated in operating con-
dition ,operational’ only.























