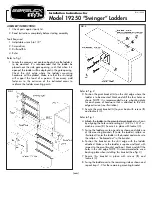
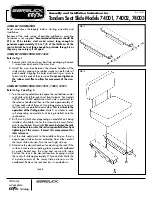
Brake Systems Application Guide
INTRODUCTION
When selecting the proper brake for a specific application, there are several factors to consider; a
few that need to be reviewed are brake torque, stopping time and/or deceleration rates, brake
mounting, brake location, thermal rating, environment, and brake style.
The brake systems manufactured by Gemco Industrial Brake Products are external friction
brakes. Applications for which these brakes are suited can be classified into two general
categories: non-overhauling and overhauling.
A) Non-overhauling loads are typically horizontally moving masses such as crane
bridges, crane trolleys, and horizontal conveyors.
B) Overhauling loads tend to “run up” in speed if a brake is not present, examples of
which are crane hoists, winches, lifts, and downhill conveyors.
Type A (non-overhauling) loads require brake torque only to stop the load and will remain at rest
due to friction. Type B (overhauling) loads have two torque requirements; the first is braking
torque required to stop the load, and the second is the torque required to hold the load at rest.
SELECTING BRAKE TORQUE BASED ON MOTOR DATA
The full -load torque of a motor is a function of horsepower and speed and is commonly used to
determine a brake torque rating. The brake torque rating is to equal or exceed the full load torque
of a motor. The formula to calculate the full load motor torque is as follows:
5250 x HP x S.F.
T =
RPM
where:
5250 =
constant
HP
=
motor horsepower
RPM =
speed of motor shaft
S.F. =
application service factor
T
=
static brake torque
CRANE
HOIST BRAKING TORQUE
Sizing of crane hoist brakes is typically based upon full load hoisting torque. The following is a
brief summary of guidelines for hoist brakes.
Each hoist on a crane should be equipped with at least one spring-set magnetic brake; hoists
handling hot metal should be equipped with more than one brake. Brake rating expressed as a
percent of hoisting torque at the point of brake application should be no less than the following:
1) 150%
when only one brake is used.
2) 150%
when multiple brakes are used and the hoist is not used to handle hot metal.
Failure of any one brake shall not reduce braking torque below 100%.
3) 175%
for hoists handling hot metal. Failure of any one brake shall not reduce brake
torque below 125%
.
9
Содержание Gemco TM 43
Страница 1: ......