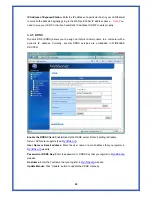
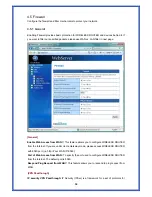
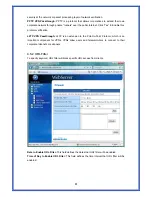
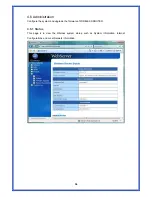
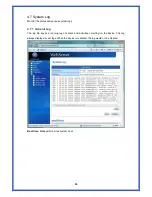
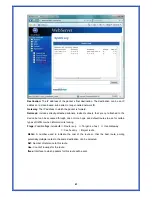
Destination:
The IP address of the packet’s final destination. The destination can be an IP
address or a class-based, sub-netted, or super-netted network ID.
Gateway:
The IP address to which the packet is forward.
Netmask:
Includes directly-attached subnets, indirect subnets that are not attached to the
device but can be accessed through one or more hops, and default routes to use for certain
types of traffic or when information is lacking.
Flags:
Possible flags include
Î
U
: Route is up.
H
: Target is a host.
G
: Use Gateway
C
: Cache entry
!
:Reject route
Metric:
A number used to indicate the cost of the route so that the best route, among
potentially multiple routes to the same destination, can be selected.
Ref:
Number of reference to this route.
Use:
Count of lookups for the route.
Iface:
Interface to which packets for this route will be sent.
41