06-06-V6-smn
p5
•
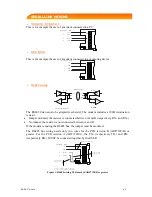
MODEM / DTE RS232
This is for example the case of a modem connected to a PC
TX
R
X
N° / SUB-D 9
NOM
+ Vcc
5
GND
2
RXD
3
TXD
+
-
RX
TX
INHIB
RTS
C TS
TX+
TX-
RX+
RX-
•
DCE RS232
This is for example the case of a modem connected to a measuring device.
TX
R
X
N° / SUB-D 9
NO M
+ Vcc
5
GND
3
RXD
2
TXD
+
-
RX
TX
INH IB
RTS
CTS
TX+
TX-
RX+
RX-
•
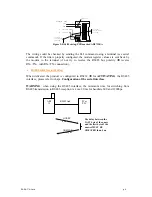
RS485 wiring
100
Ω
Rt
Jumper
B
A
B’ / Z
A’ / Y
R
T
B / RX-
A / RX+
Z / TX-
Y / TX+
R
T
MODEM
Network termination 485
RS485 Network
The RS485 link needs to be adapted (each side). The modem includes a 100
Ω
termination
resistor:
•
Jumper mounted, the resistor is connected between A and B (respectively RX+ and RX-)
•
No jumper, the resistor is not connected between A and B
If the modem is ending the RS485 bus, the jumper must be mounted.
The RS485 bus wiring needs only two wires for the PCB revision B (ARF7120/B) or
greater. For the PCB revision A (ARF7120/A), the TX+ (respectively TX-) and RX+
(respectively RX-) MUST be connected together by the USER.
TX
R
X
BUS RS485
NAME
+ Vcc
GND
A
TX+/RX+
B
TX-/ RX-
+
-
RX
TX
INHIB
RTS
CTS
TX+
TX-
RX+
RX-
jumper
Connect only TX-
or RX- (note 1)
Connect only TX+
or RX+ (note 1)
PCB revision B or greater
AR
F7120/
B
Note 1:
¾
TX- is connected to RX- on the PCB
¾
TX+ is connected to RX+ on the PCB
Figure 1: RS485 wiring, PCB marked ARF7120/B or greater
SERIAL LINK WIRING