7
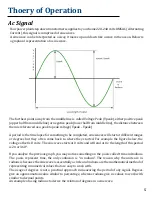
In North America the voltage RMS is 120v or 115v for common appliances to run on, however the
peak voltage is 120v *√2 = 170 Peak Voltage. Therefore the furthest point form the middle is not
120v AC, it is 170v AC!
RMS (root mean squared) is the terminology to best describe mathematically a constant alternating
voltage that is being delivered. Since the maximum peak will be 170 volts both positive and
negative, the average of the voltage supplied during any cycle will be below 170 volts. Therefore
the terminology of RMS acts mathematically as a steady amount of AC voltage that will be supplied
to any load.
If an incandescent light bulb is rated to for 60 volts AC and the line measured indicates it provides
60 volts peak then the RMS is 60V* 1/√2 = 42.42 volts RMS, however there is another line with a
label indicating it has a 85 volts peak then the RMS is 85V*1/√2=60.095 volts RMS. It is clear that
the 60.095 stable Volts will shine brighter than the stable 42.42 volts.
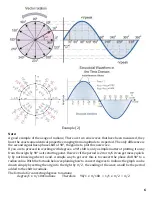
The average voltage is the representation mathematically to find the midpoint of the AC voltage or
current that is being provided during time lapse of the period. The difference between RMS and
Average is with the fact that RMS is the instantaneous value rooted and average is the instantaneous
voltage added together divided by the total number of instantaneous voltage measured in the
period. Both mathematical representations are used to describe the output AC voltage or current
compared to the DC voltage and current.
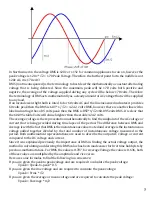
Since it was explained previously the importance of RMS in finding the actual voltage output, the
method in calculating and deriving this RMS value has been made easier for first time hobbyists by
previous mathematicians. For RMS the value is 0.707, for Average Voltage the value is 0.636, both
of these values are multiplied by the amplitude and vice versa.
Here are some formulas to find the following in a sine wave;
If you are given the peak to peak voltage and are required to calculate the peak voltage:
Vpeak = Vpeak-to-peak * 0.5
If you are given the rms voltage and are required to calculate the peak voltage:
Vpeak = Vrms * √2
If you are given the average or mean voltage and are required to calculate the peak voltage:
Vpeak = Vaverage * π/2
Содержание AK-10
Страница 16: ......