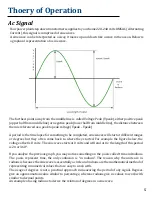
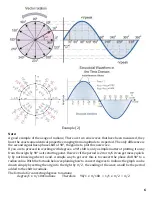
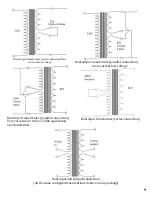
6
Example (2)
Note:
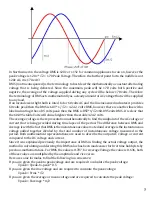
A good example of the usage of radians; There are two sine waves that have been measured, they
have the exact same identical properties ranging from amplitude to its period. The only difference is
the second signal has a phase shift of 90°, the goal is to plot this new wave.
If you are to proceed in working with degrees, a 90° shift is only a simple matter of plotting it away
from the origin by 90° as its starting point. However if the period is 2π or π/6 it can get messy quick
-
ly by not knowing where to end. A simple way to get over this is to convert the phase shift 90° to a
radian value. With the formula below explaining how to convert degrees to radians the graph can be
drawn simply by setting the origin to the right by π/2 , the ending of the wave would be the period
added to the shift in radians.
The formula for converting degrees to radians:
degree/1 x π/180=radians
Therefore 90/1 x π/180 = 1/1 x π/2 = π/2
Содержание AK-10
Страница 16: ......