QoS Classifiers
483
QoS Classifiers
You define classifiers to distinguish certain types of traffic from other
types of traffic. A classifier tells the system how to identify a certain type
of traffic; after defining a classifier, you must apply a control to the
classifier.
Important
Considerations
Review the following before configuring classifiers:
■
You can classify bridged or routed traffic (such as AppleTalk or IPX)
based on protocol type, cast type, and IEEE 802.1p priority. For routed
IP traffic, you can also classify traffic by IP source addresses,
destination addresses, or TCP or UDP sockets.
■
Before you define a classifier, determine whether you can use one of
the system’s predefined classifiers (classifiers that come with your
system). If you decide to define your own classifier, you need to decide
which type of classifier to define,
flow
(IP routed traffic only) or
nonflow
(bridged or routed traffic).
■
You can define up to
100
flow classifiers and up to
16 nonflow
classifiers. Because the system predefines 16 nonflow classifiers, you
must delete one of the existing nonflow classifiers (except the default
classifier) before you can add your own. See “Modifying and
Removing Classifiers and Controls” later in this chapter for
information on changing or deleting a classifier.
■
When you configure a classifier, the system prompts you for different
information based on your choice of defining a flow or nonflow
classifier.
Using Predefined
Classifiers
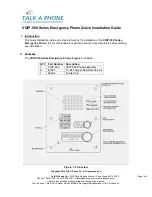
Figure 82 shows a QoS classifier summary from the Administration
Console with the 2 predefined flow classifiers (FTP and Telnet) and
16 predefined nonflow classifiers, along with their associated controls.
(You can use your configuration tool to display summary and detail
information for your classifiers.)
The system provides a default classifier (499). You cannot remove or
modify this classifier
. If you want to
modify one of the predefined
nonflow classifiers with controls, you must remove the control first.
In Figure 82, U refers to unicast, M refers to multicast, and B refers to
broadcast. Also, the range 0–7 implies that a nonflow classifier
recognizes
all
IEEE 802.1p priority tags. (See Table 59 earlier in this guide.)
Содержание CoreBuilder 3500
Страница 44: ...44 CHAPTER 2 MANAGEMENT ACCESS ...
Страница 58: ...58 CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM PARAMETERS ...
Страница 86: ...86 CHAPTER 5 ETHERNET ...
Страница 112: ...112 CHAPTER 6 FIBER DISTRIBUTED DATA INTERFACE FDDI ...
Страница 208: ...208 CHAPTER 9 VIRTUAL LANS ...
Страница 256: ...256 CHAPTER 10 PACKET FILTERING ...
Страница 330: ...330 CHAPTER 12 VIRTUAL ROUTER REDUNDANCY PROTOCOL VRRP ...
Страница 356: ...356 CHAPTER 13 IP MULTICAST ROUTING ...
Страница 418: ...418 CHAPTER 14 OPEN SHORTEST PATH FIRST OSPF ...
Страница 519: ...RSVP 519 Figure 94 Sample RSVP Configuration Source station End stations Routers ...
Страница 566: ...566 CHAPTER 18 DEVICE MONITORING ...
Страница 572: ...572 APPENDIX A TECHNICAL SUPPORT ...
Страница 592: ...592 INDEX ...