Digital Operator Display Functions and Levels5-3
5-
3
Digital Operator Display Functions and Levels
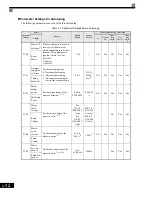
The following figure shows the Digital Operator display hierarchy for the Drive.
MENU
Drive Mode
Drive can be operated and its
status can be displayed.
Quick Programming Mode
Minimum parameters required
for operation can be monitored
or set.
Advanced Programming Mode
All parameters can be moni-
tored or set.
Verify Mode
Parameters changed from the
default settings can be moni-
tored or set.
Autotuning Mode
Automatically sets motor
parameters if autotuning data
(from motor nameplate) is
input for open-loop vector con-
trol or to measure the line-to-
line resistance for V/f control.
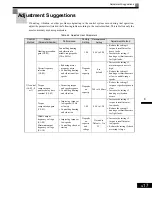
No.
Function
Display
U1
Status Monitor Parameters
Monitor
U2
Fault Trace
Fault Trace
U3
Fault History
Fault History
A1
Initialize Mode
Initialization
A2
User-specified Setting Mode
User
Parameters
b1
Operation Mode Selections
Sequence
b2
DC Injection Braking
DC Braking
b3
Speed Search
Speed Search
b4
Timer Function
Delay Timers
b5
PID Control
PID Control
b6
Dwell Functions
PID Control
b7
Droop Control
Droop Control
b8
Energy Saving
Energy
Saving
b9
Zero Servo
Zero Servo
C1
Acceleration/Deceleration
Accel/Decel
C2
S-curve Acceleration/Deceleration
S-Curve Accel
C3
Motor Slip Compensation
Motor-Slip
Comp
C4
Torque Compensation
Torque Comp
C5
Speed Control (ASR)
ASR Tuning
C6
Carrier Frequency
Carrier Freq
d1
Preset Reference
Preset
Reference
d2
Reference Limits
Reference
Limits
d3
Jump Frequencies
Jump
Frequencies
d4
Reference Frequency Hold
Sequence
d5
Torque Control
Torque Control
d6
Field Control
Field-
weakening
E1
V/f Pattern
V/f Pattern
E2
Motor Setup
Motor Setup
E3
Motor 2 V/f Pattern
V/f Pattern 2
E4
Motor 2 Setup
Motor Setup 2
F1
PG Option Setup
PG Option
Setup
F2
Analog Reference Card
AI-14 Setup
F3
Digital Reference Card
DI-08, 16 Setup
F4
Analog Monitor Cards
AO-08, 12
Setup
F5
Digital Output Card
DO-02,08
Setup
F6
Communications Option Card
CP-916 Setup
H1
Multi-function Contact Inputs
Digital Inputs
H2
Multi-function Contact Outputs
Digital
Outputs
H3
Analog Inputs
Analog Inputs
H4
Multi-function Analog Outputs
Analog
Outputs
H5
MODBUS Communications
Serial Com
Setup
H6
Pulse Train
Pulse I/O Setup
L1
Motor Overload
Motor
Overload
L2
Power Loss Ridethrough
PwrLoss
Ridethru
L3
Stall Prevention
Stall
Prevention
L4
Reference Detection
Ref Detection
L5
Fault Restart
Fault Restart
L6
Torque Detection
Torque
Detection
L7
Torque Limits
Torque Limit
L8
Hardware Protection
Hdwe
Protection
n1
Hunting Prevention Function
Hunting Prev
n2
Speed Feedback Protection Control
AFR
n3
High-slip Braking
High Slip
n4
Speed Estimation
Observer
n5
Feed Forward
Feedfoward
Cont
o1
Monitor Select
Monitor Select
o2
Multi-function Selections
Key
Selections
o3
Copy Function
COPY
Function
T1
Motor Autotuning
Auto-Tuning
Summary of Contents for CIMR-G7U
Page 2: ......
Page 7: ...v...
Page 32: ...1 18...
Page 90: ...3 16...
Page 112: ...4 22...
Page 382: ...6 164...
Page 410: ...7 28...
Page 454: ......
Page 455: ......