13
English
1
Set the VOLUME control to minimum.
2
Turn on the power supply to all the components.
3
Play any source and adjust the amplifier’s volume control
to the desired listening level.
4
Increase the volume gradually to adjust the volume
balance between this unit and the main speakers.
5
If necessary, you may set the HIGH CUT switch to the
HIGH position.
Notes
•
Once the volume balance between the subwoofer and the
main speakers is adjusted, you can adjust the volume of
your whole sound system by using only the amplifier’s
volume control.
However, if you change the main speakers NS-M103 to
others, you must make this adjustment again.
•
For adjusting the VOLUME control and the HIGH CUT
switch, refer to “FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS” shown
below.
Note about setting the HIGH CUT switch
This system is designed so that the optimum tone balance
between the subwoofer and the main speakers is obtained
when this switch is set to the LOW position. However, the tone
balance may change depending on the room size, the distance
from the subwoofer to the main speakers, and so on.
So, if necessary, switch it to the HIGH position.
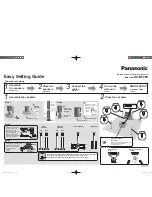
ADJUSTMENT BEFORE USING THE SUBWOOFER
Before using the subwoofer, make an adjustment on the subwoofer to obtain the optimum volume and tone balance between the
subwoofer and the main speakers by following the procedures shown below.
INPUT2
HIGH CUT
AUTO
STANDBY
STANDBY-RED
ON-GREEN
OFF
LOW
HIGH
LOW
HIGH
OUTPUT
TO SPEAKERS
INPUT1
FROM AMPLIFIER
INPUT2
HIGH CUT
AUTO
STANDBY
STANDBY-RED
ON-GREEN
OFF
LOW
HIGH
OFF
POWER
ON
LOW
HIGH
VOLUME
0
10
VOLUME
0
10
1, 4
5
2
Fig. 1 shows the frequency characteristics of the subwoofer
with each position (HIGH/LOW) of the HIGH CUT switch.
Fig. 2 shows the optimum volume level with the HIGH CUT
switch at the LOW position and its frequency characteristics
when this subwoofer is combined with NS-M103 (main
speakers).
■
FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS
20
50
100
200
500Hz
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
HIGH CUT
LOW
HIGH CUT
HIGH
20
50
100
200
500Hz
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
SW-P30
NS-M103
HIGH CUT
LOW
HIGH
VOLUME
0
10
Fig. 1
Fig. 2