XC4000 Series Field Programmable Gate Arrays
4-50
September 18, 1996 (Version 1.04)
Boundary Scan
The ‘bed of nails’ has been the traditional method of testing
electronic assemblies. This approach has become less
appropriate, due to closer pin spacing and more sophisti-
cated assembly methods like surface-mount technology
and multi-layer boards. The IEEE Boundary Scan Stan-
dard 1149.1 was developed to facilitate board-level testing
of electronic assemblies. Design and test engineers can
imbed a standard test logic structure in their device to
achieve high fault coverage for I/O and internal logic. This
structure is easily implemented with a four-pin interface on
any boundary scan-compatible IC. IEEE 1149.1-compati-
ble devices may be serial daisy-chained together, con-
nected in parallel, or a combination of the two.
The XC4000 Series implements IEEE 1149.1-compatible
BYPASS, PRELOAD/SAMPLE and EXTEST boundary
scan instructions. When the boundary scan configuration
option is selected, three normal user I/O pins become ded-
icated inputs for these functions. Another user output pin
becomes the dedicated boundary scan output. The details
of how to enable this circuitry are covered later in this sec-
tion.
By exercising these input signals, the user can serially load
commands and data into these devices to control the driv-
ing of their outputs and to examine their inputs. This
method is an improvement over bed-of-nails testing. It
avoids the need to over-drive device outputs, and it reduces
the user interface to four pins. An optional fifth pin, a reset
for the control logic, is described in the standard but is not
implemented in Xilinx devices.
The dedicated on-chip logic implementing the IEEE 1149.1
functions includes a 16-state state machine, an instruction
register and a number of data registers. The functional
details can be found in the IEEE 1149.1 specification and
are also discussed in the Xilinx application note XAPP 017:
"
Boundary Scan in XC4000 Devices."
shows a simplified block diagram of the
XC4000E Input/Output Block with boundary scan imple-
mented. XC4000EX boundary scan logic is identical.
is a diagram of the XC4000-Series
boundary scan logic. It includes three bits of Data Register
per IOB, the IEEE 1149.1 Test Access Port controller, and
the Instruction Register with decodes.
XC4000-Series devices can also be configured through the
boundary scan logic. See
Boundary Scan Pins” on page 64
Data Registers
The primary data register is the boundary scan register.
For each IOB pin in the FPGA, bonded or not, it includes
three bits for In, Out and 3-State Control. Non-IOB pins
have appropriate partial bit population for In or Out only.
PROGRAM, CCLK and DONE are not included in the
boundary scan register. Each EXTEST CAPTURE-DR
state captures all In, Out, and 3-state pins.
The data register also includes the following non-pin bits:
TDO.T, and TDO.O, which are always bits 0 and 1 of the
data register, respectively, and BSCANT.UPD, which is
always the last bit of the data register. These three bound-
ary scan bits are special-purpose Xilinx test signals.
The other standard data register is the single flip-flop
BYPASS register. It synchronizes data being passed
through the FPGA to the next downstream boundary scan
device.
The FPGA provides two additional data registers that can
be specified using the BSCAN macro. The FPGA provides
two user pins (BSCAN.SEL1 and BSCAN.SEL2) which are
the decodes of two user instructions. For these instruc-
tions, two corresponding pins (BSCAN.TDO1 and
BSCAN.TDO2) allow user scan data to be shifted out on
TDO. The data register clock (BSCAN.DRCK) is available
for control of test logic which the user may wish to imple-
ment with CLBs. The NAND of TCK and RUN-TEST-IDLE
is also provided (BSCAN.IDLE).
Instruction Set
The XC4000-Series boundary scan instruction set also
includes instructions to configure the device and read back
the configuration data. The instruction set is coded as
shown in
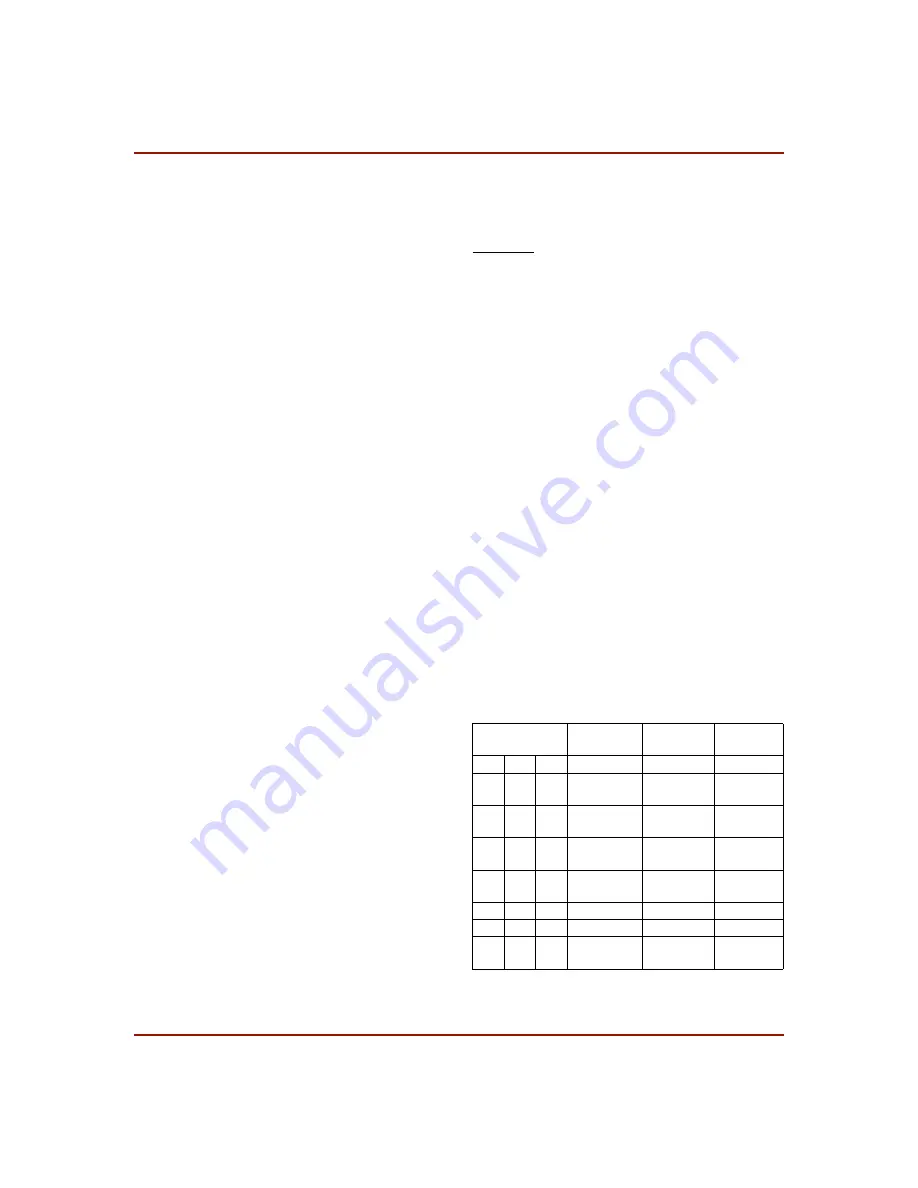
Table 19: Boundary Scan Instructions
Instruction
I2 I1 I0
Test
Selected
TDO Source
I/O Data
Source
0
0
0
EXTEST
DR
DR
0
0
1
SAMPLE/
PRELOAD
DR
Pin/Logic
0
1
0
USER 1
BSCAN.
TDO1
User Logic
0
1
1
USER 2
BSCAN.
TDO2
User Logic
1
0
0
READBACK Readback
Data
Pin/Logic
1
0
1
CONFIGURE
DOUT
Disabled
1
1
0
Reserved
—
—
1
1
1
BYPASS
Bypass
Register
—
























