-17-
Model W1834 (For Machines Mfd. Since 7/14)
O
PE
R
ATIO
NS
Wheel.Selection
Your Model W1834 uses only Type 5 grinding wheels that
have a
1
⁄
2
" bore, are 6" in diameter and 1
1
⁄
2
" thick.
Aluminum oxide and silicon carbide wheels are typically
marked in a uniform manner by all major manufacturers.
Understanding these markings will help you understand
the capabilities of various wheels.
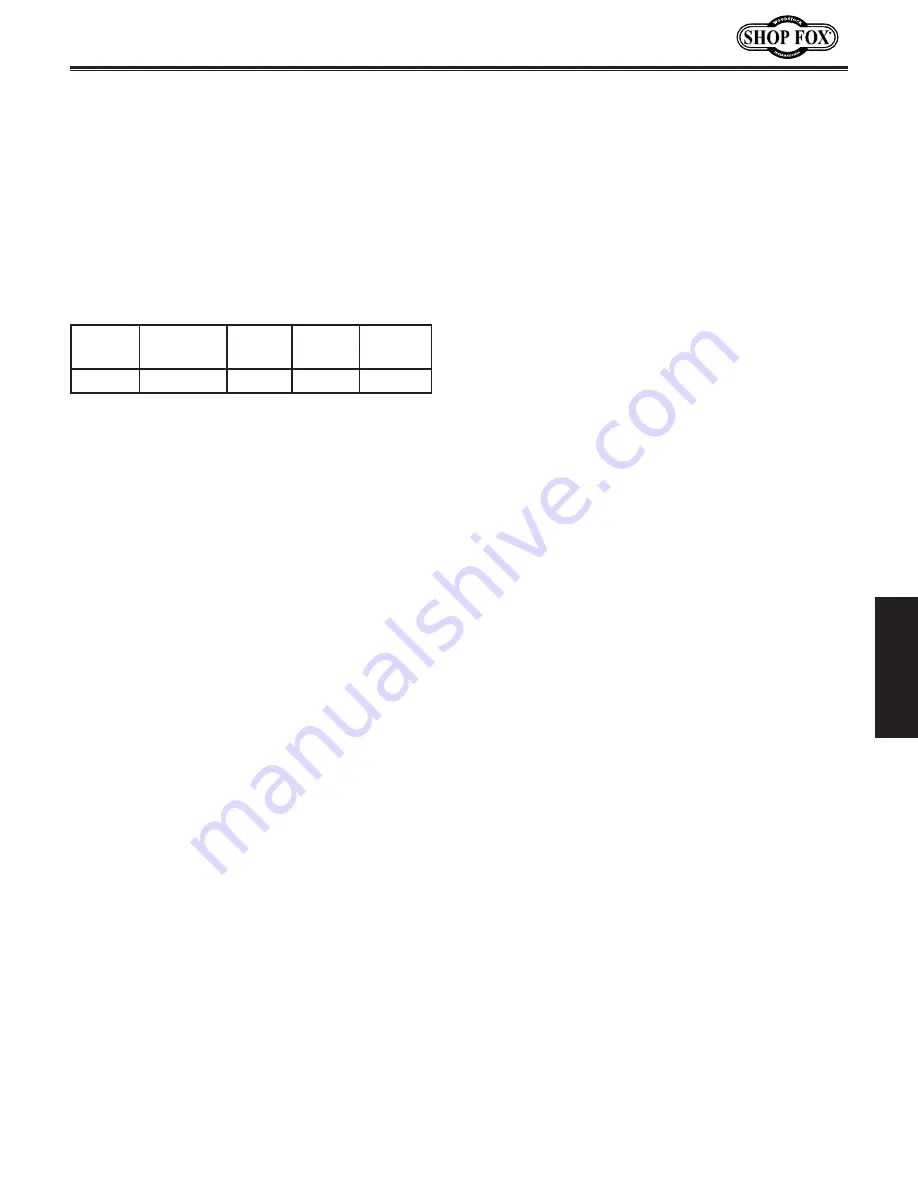
The.typical.format.for.wheel.numbering.is:
Type
Abrasive
Type
Grit
Size
Grade
Bond
Type
5
A
100
K
V
•. Type:.
Refers to a particular wheel configuration,
such as Type 5, which has a recessed center for the
top-mounting flange.
•
Abrasive.Type:.
Refers to the abrasive grain of the
wheel. The most common types are
A
for aluminum
oxide,
C
for silicon carbide, and
SG
for seeded gel.
•
. Grit.Size:.
Refers to the size of the abrasive grain in
the wheel. The lower the number, the coarser the
wheel.
•
Grade:.
Indicates the hardness of the wheel, with
A
being the softest and
Z
being the hardest.
•
Bond.Type:.
Refers to the type of bonding material
used to hold the abrasive grain. Most general-
purpose wheels will have a
V
, indicating vitrified
clay, which provides high strength and good porosity.
The other common bond type is
B
for synthetic
resins, which are generally used to grind cemented
carbide and ceramic materials.
Note:.
There may be other numbers or letters that have
meaning for a particular type of wheel. Always refer
to the manufacturer's technical data for a complete
explanation when choosing a grinding wheel.
Wheel.Care
Your safety depends on the condition of the
wheel during operation. A wheel in poor
condition increases the risk of flying apart
and injuring the operator or causing prop-
erty damage.
To.reduce.the.risk.of.breaking.the.wheel:
• Always transport, store, and handle
wheels with care. Wheels could be
damaged if they are dropped or if
heavy objects are stacked on them.
• DO NOT grind materials that are not
correct for the wheel type.
• If a grinding wheel rotates faster
than its RPM rating, it could fly apart
during operation.
• Mount wheels properly (refer to
Wheel.
Replacement
on
Page.27
for detailed
instructions). Never use a wheel with
the wrong bore size for the machine.
• Do not abuse the wheel by jamming
work into the grinding wheel with
excessive force or by allowing
workpiece to become overly hot
during operation.
• Do not store wheels in a damp or wet
location that will damage the bonding
material.
• Replace the wheel when it becomes
less than
1
⁄
2
of its original thickness or
less than
3
⁄
4
".
• Use only the wheel flanges that are
included with the grinder.
• To ensure good grinding results, dress
the wheel often (refer to
Wheel.
Dressing
on
Page.26
for instructions).
• Always inspect and perform
the ring test before installing any
grinding wheel (refer to
Wheel.
Inspection.&.Ring.Test.
on
Page.18
for
detailed instructions).
















































